How does a laser printer work?
Laser printers have become indispensable attributes of office equipment. Such popularity is due to high speed and low cost of printing. To understand how this technique works, you should know the structure and operation of the laser printer. In fact, all the magic of the device is explained by simple design solutions.
Content
The history of laser printing equipment
Back in 1938, Chester Carlson patented a technology that transferred the image to paper using dry ink. The main engine of the work was static electricity. Electrographic method (and it was he) received wide distribution in 1949, when Xerox took it as a basis for the work of its very first apparatus.However, to logical perfection and complete automation of the process, another ten years of work was required - only after that the first Xerox appeared, which became the prototype of modern laser printing devices.

The first Xerox 9700 laser printer
The very first laser printer appeared only in 1977 (it was the Xerox 9700 model). Then the printing was done at a speed of 120 pages per minute. This device was used exclusively in institutions and enterprises. And already in 1982, the first Canon desktop unit was released. From this time on, numerous brands are connected to the development, and to this day they offer all new options for desktop laser printing assistants. Every person who decides to use such equipment will be interested to learn more about the internal structure and the principle of operation of such a unit.
What's inside
Despite the large range, the laser printer device of all models is similar. The basis of the work taken photoelectric part of xerographyand the device itself is divided into the following blocks and units:
- laser scanning unit;
- node transferring the image;
- node to fix the image.
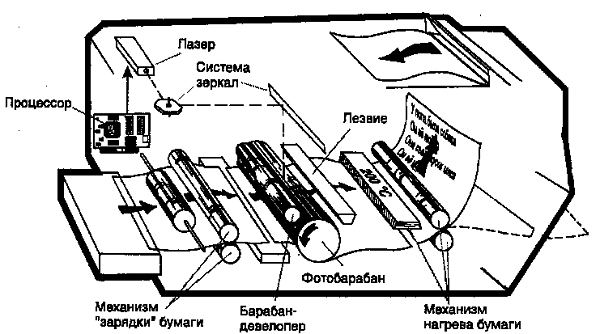
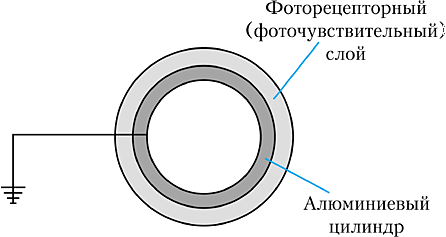
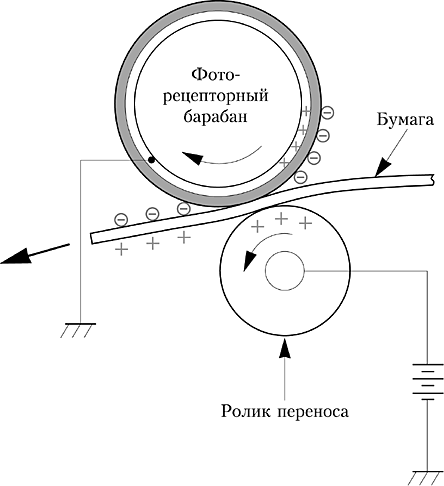
The first block is presented lens and mirror system. This is where the semiconductor type of laser with a focusable lens is located. Next are the mirrors and groups that can rotate, thereby forming an image. Go to the node responsible for the transfer of the image: it is itself toner cartridge and rollercarrying charge. Already in the cartridge there are three main image-forming elements: a photo cylinder, a pre-charged shaft and a magnetic shaft (working in conjunction with the device’s drum). And it is here that the possibility of a photo-cylinder to change its conductivity under the action of the light that fell on it is becoming more important. When a charge is attached to a photo-cylinder, it keeps it for a long time, but when exposed to light, its resistance decreases, which causes the charge to begin to drain from its surface. This is how the impression we need appears.
In general, there are two ways to create a picture.
- Virtually all laser printers are used positive charge toners - here the laser will highlight areas with a potential image arrangement.This is the principle of operation of the laser printer brands HP, Canon, Xerox. This provides fine image detail.
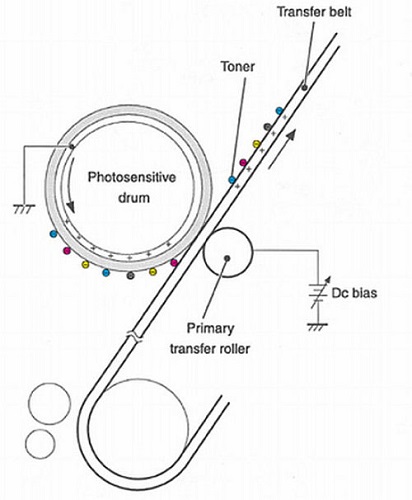
Color Printing Theory HP-2500
- Epson, Kyocera, Brother are already in use. negative charge toner - the laser highlights only those areas where it is not supposed to be. With this technology, the winner is a uniform fill image.
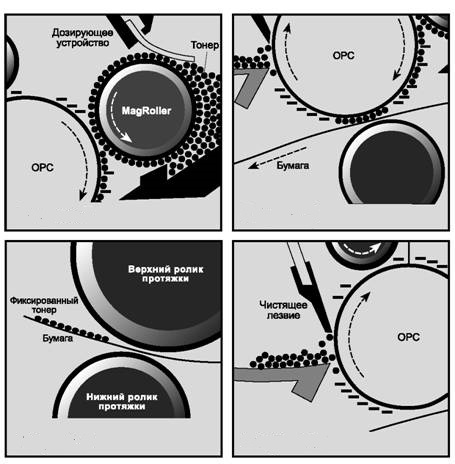
The principle of printing toner with a negative charge
Getting into the unit, just before the future contact with the photo-cylinder, the paper itself receives the corresponding charge. This helps her transfer video. After transfer, the static charge disappears with the help of a special neutralizer - this is how the paper ceases to be attracted to the photo cylinder.
And how is the image fixed? This is due to those additives that are in the toner. They have a specific melting point. Such a “stove” presses the melted toner powder into the paper, after which it quickly hardens and becomes durable.
Printed on paper with a laser printer images have excellent resistance to numerous external influences.
How does the cartridge
The cartridge is the decisive link in the operation of a laser printer. It is a small bunker with two compartments - for working toner and for already spent material. There is also a photosensitive drum (photo cylinder) and mechanical gears for turning it.
The toner itself is a powder of a fine-dispersed type, which consists of polymer balls - they are covered with a special layer of magnetic material. If we are talking about color toner, then it also includes dyes.
It is important to know that each manufacturer produces its own original toner - all of them have their own magnetism, dispersion and other properties.
That is why in no case can you refill cartridges with random toners - this may adversely affect its performance.
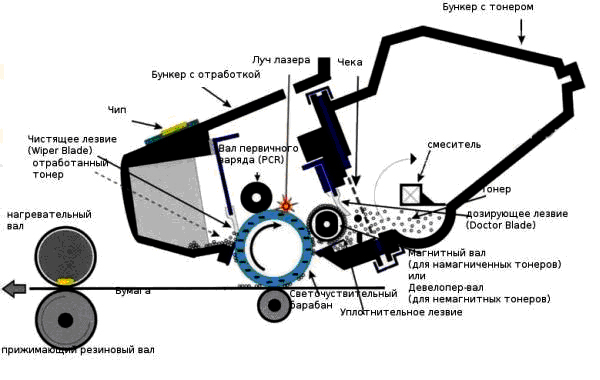
Imprint birth process
The appearance of the image or text on paper will consist of the following successive stages:
- drum charge;
- exposure;
- development;
- transfer;
- fastening.
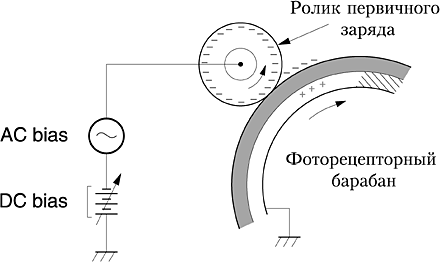
Drum charge
How does the photo charge work? It is formed on a photodrum (where, as is already clear, the very future of the image is born).To begin with, there is a supply of charge, which can be both negative and positive. This happens in one of the following ways.
- Used by coronator, that is, a tungsten filament with a coating of carbon, gold and platinum inclusions. When a high voltage comes into play, a discharge rushes between this thread of the carcass, which, accordingly, will create an electric field transferring the charge to the photodrum.
- However, the use of yarn led over time to problems with contamination and deterioration in the quality of printed material. Much better acts charge roller with similar features. He himself looks like a metal shaft, which is covered with conductive rubber or foam rubber. There is a contact with the photocylinder - at this moment the video and transfers the charge. The voltage here is much lower, but parts wear out much faster.
Exposure
This is the work of lighting, with the result that part of the photo-cylinder becomes conductive and passes a charge through the metal base in the drum. And the area subjected to exposure becomes uncharged (or acquires a weak charge). At this stage, an invisible image is formed.
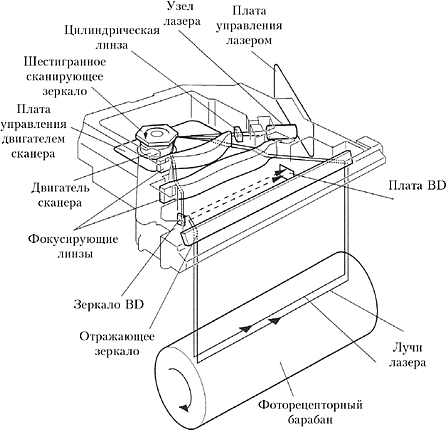
Technically, this is done so.
- The laser beam falls on the surface of the mirror and is reflected on the lens, which will distribute it to the required place on the drum.
- So the system of lenses and mirrors forms a line along the photo-cylinder - the laser turns on, then turns off, the charge remains intact, then it is removed.
- Is the line over? The drum unit turns around and the exposure continues again.
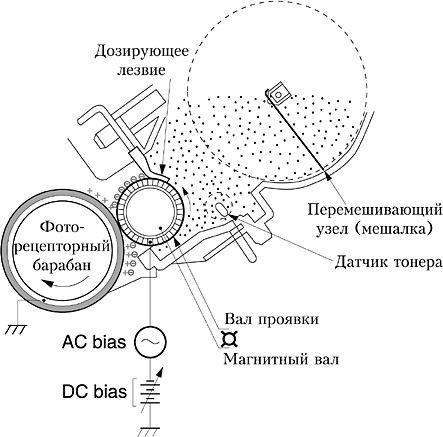
Developing
In this process is of great importance magnetic shaft from cartridge, similar to a tube of metal, inside of which there is a magnetic core. Part of the surface of the shaft is placed in the filling toner hopper. The magnet attracts powder to the shaft, and it is carried out.
It is important to adjust the uniform distribution of the powder layer - for this there is a special dosing blade.. It skips only a thin layer of toner, throwing the rest back. If the blade is installed incorrectly, black streaks may appear on the paper.
After that, the toner moves to the area between the magnetic shaft and the photo-cylinder - here it will be attracted to the exposed areas, and will push away from the charged ones. So the image becomes more visible.
Transfer
To make the image appear on paper transfer roller, in the metal core of which a positive charge is attracted - it is transferred onto the paper due to a special rubberized coating.
So, the particles are detached from the drum and begin to move to the page. But they are kept here so far only because of static voltage. Figuratively speaking, the toner is simply poured in the right place.
Dust and lint from paper can get into the toner, but they are removed. viper (special plate) and sent straight to the waste compartment in the bunker. After a full circle of the drum, the process is repeated.
Pin image
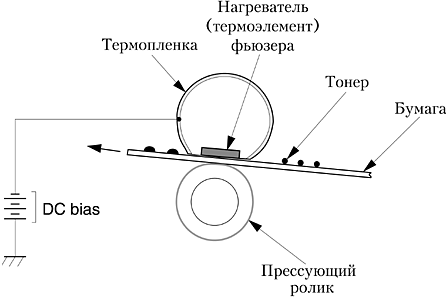
For this purpose, the toner property is melted at high temperatures. Structurally, this is assisted by the following two shaft:
- in the upper is the heating element;
- molten toner is pressed into the bottom of the paper.
Sometimes such a "stove" is thermal film - special flexible and heat-resistant material with a heating component and a pressure roller. Its heating is controlled by the sensor.Just at the moment of passage between the film and the presser part of the paper and warmed up to 200 degrees, which allows it to easily absorb the liquid toner.
Further cooling takes place in a natural way - in laser printers it is usually not necessary to install an additional cooling system. However, a special cleaner passes here again - usually its role is played by felt shaft.
Felt is usually impregnated with a special compound that helps lubricate the coating. Therefore, another name for such a shaft is oil.
How color laser printing is performed
But what about color printing? The laser device uses four such primary colors — black, magenta, yellow, and cyan. The principle of printing is the same as in the black and white case, but first the printer breaks the image into monochrome for each color. The consecutive transfer of a different color by each cartridge begins, and as a result of blending, the desired result is obtained.
There are such technologies of color laser printing:
- multipass;
- single pass
At multi-pass option An intermediate carrier comes into play — a shaft or ribbon that carries toner.It works like this: 1 color is superimposed for 1 revolution, then another cartridge is fed to the right place, and the second is placed on top of the first picture. Four passes are enough to form a full-fledged picture - it will go over to paper. But the device itself will work 4 times slower than its black-and-white fellow.
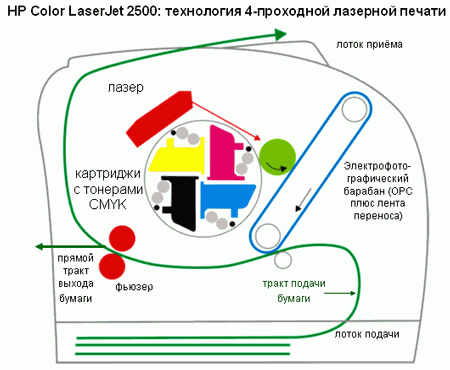
HP 4-way laser printing technology
How does the printer work with single pass technology? In this case, all four separate printing mechanisms have a common control - they are lined up in one line, each has its own laser unit with a portable roller. So paper and goes on the drum, consistently collecting all four images of cartridges. Only after this passage, the sheet goes into the oven, where the picture is fixed.
The advantages of laser printers have made them favorites for working with documentation, both in the office and at home. And information about the internal component of their work will help any user to notice shortcomings in time and contact the customer service for technical support of the device.

/rating_off.png)











