Classification of 3D printers
The emergence of 3d printers has opened a new era of technology - it has now become possible to print a voluminous item. The purpose of the resulting three-dimensional products can be very different - from toys to medical prostheses. The basis of the work is taken digital model (or drawing), which is then embodied in its exact real copy. Such devices are found in different capacities and configuration, in home and industrial versions. Existing to date types of 3D printers use a variety of materials to get bulk printing.
Content
Classification of printers by type of materials used
A consumable consumable determines the types of 3d-printers. Laser aggregates sinter and laminate the powder. Jet The 3d printer alternately glues the layers of the source material used, then sintering it. The next step is cooling. Here types of photopolymer plastic, resins, powders, silicone, metal and wax components can be used. Consider how this technique works on different materials.
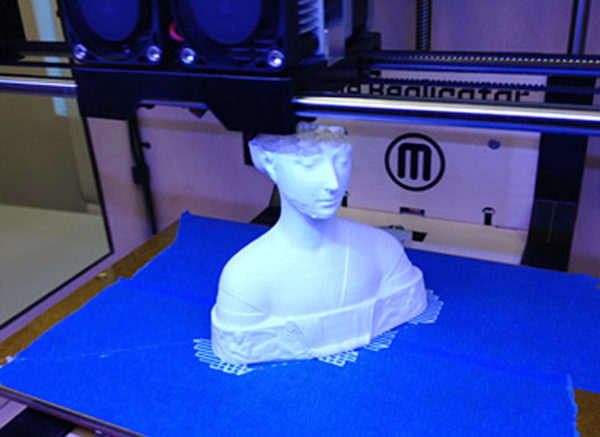
Powder
The principle of operation of the technique is manifested in the following actions:
- based on the model provided, the print head begins to apply a special binder to certain places;
- a thin roller will be applied to the powder, which is sintered with the substance.
- Further process repeats.
Such a device is quite real assemble with your own hands - it is enough to have the necessary components. Another bonus "in the piggy bank" of such a device is the work with metal powder.
Gypsum
The gypsum version is also filled with powders, but already relevant - from gypsum to putty, cement and the like. Required binder. Such printers are most often used in the creation of interior decorations. Products here are very diverse.

Photopolymer
For the manufacture of objects in this case, liquid photopolymers are used. Interesting principle creating figurines. Focusing on the computer model, the ultraviolet laser will illuminate certain places. In the future, they will harden under the action of ultraviolet radiation. Such an illumination will be carried out through a specially prepared photomask - only here will the ultraviolet lamp be used. Template blanks will change with each new layer.
If the technique is chosen stereolithographic, then you can enjoy high precision of the performance of bulk printing. The only negative is low speed, but if accuracy is a relevant indicator, then they do not pay attention to the execution time.

Wax
Such a device prints with the help of wax - a material with a low melting temperature. This property has its own bonus - the ease of operation. That is why the clarity and accuracy of the contours performed is immaculate.
How to achieve color
To make objects of the most different colors, the technique uses a special head. There are several here extruders - components capable of melting and depositing the consumable used.
Most of these units are involved in the manufacture of children's toys.Another purpose - the creation of designer jewelry.
There is another way called "sublimation". This type of printer is used if it is necessary to transfer an image (for example, from a photo) to a relief surface. To realize what was intended in certain places, dyes are heated - due to temperature effects, evaporation occurs and the desired pattern remains.

3D printing technology
With regard to the technologies used, a special classification is applied, which will be useful for every future owner of a 3D printer to know:
- FDM;
- Polyjet or MJM;
- LENS;
- LOM;
- SLA;
- SLS;
- 3DP;
Fdm
This is the most popular technology in the devices in question.. With FDM (fused deposition modeling), the unit will squeeze out the consumable through a special nozzle layer by layer. These include:
- makerbot-like devices;
- Stratasys printers;
- units used in cooking (dressing goes cheese products, dough, frosting);
- medical devices (medical gel with live cells).

Polyjet
Interesting and MJM (Multi Jet Modeling), which implies a technique multiple jet modeling. The process is similar to a conventional inkjet due to the flow of material through small nozzles (there may be several hundred of them). After the previous layer hardens, the specified three-dimensional model will be formed.
Consumables are photoplates and plastic, suitable and special wax. Typically, such a bulk print is used in the manufacture of medical implants, dentures and casts.
Really getting multi-color options, as well as objects with different properties, for example, elastic in combination with solid.
There are also disadvantages to using such a technology - a very expensive source material and fragile result. Application usually finds in medicine and industrial prototyping.

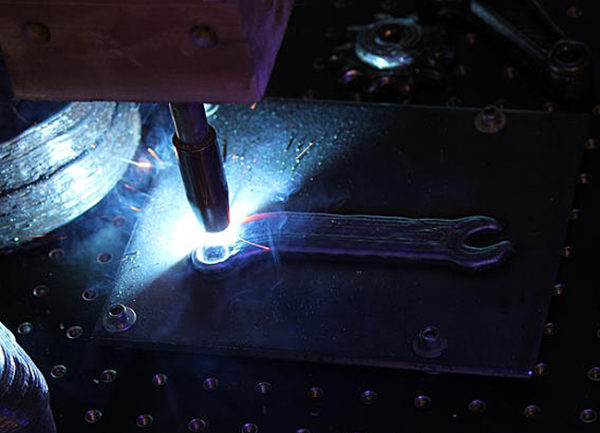
LENS
With LASER ENGINEERED NET SHAPING, the consumable consumed from the nozzle immediately falls under the focus of the laser beam, which is fraught with instant sintering. Using metal powder helped in the manufacture of objects of steel and titanium, which made it possible to operate 3D printers in the industry. Many alloys really mix and get directly in the process. For example, get turbine titanium blades for turbines.
LOM
With Laminated Object manufacturing, thin and already laminated sheets are laser cut, gluing, caking or pressing into a three-dimensional object. This way you can print plastic, aluminum and paper 3D objects.
By the way, the source for aluminum objects is the corresponding foil - it will be “sinter” with the help of ultrasonic vibration.
Despite the lightness of the source material, paper models are very durable, and their cost price will be almost penny. But immediately we must prepare for the fact that such a product will be accompanied by a large amount of waste. Although the latter can be avoided by placing several small objects at once on one sheet.
SLA
To understand how Stereolithography works, you need to imagine a bath filled with liquid polymer. A laser beam passing over its surface polymerizes the layer. After the readiness of one of the layers, the platform will lower the part so that the liquid polymer fills the voids. Then the situation changes: the detail rises to the top, and the laser itself is located below.
When working with this method, surface treatment is needed to sand and remove excess material. Sometimes the result is further baked in ultraviolet ovens.
Such a printer can not be kept at home:
- due to the toxicity of the photopolymer;
- due to the high cost of service.

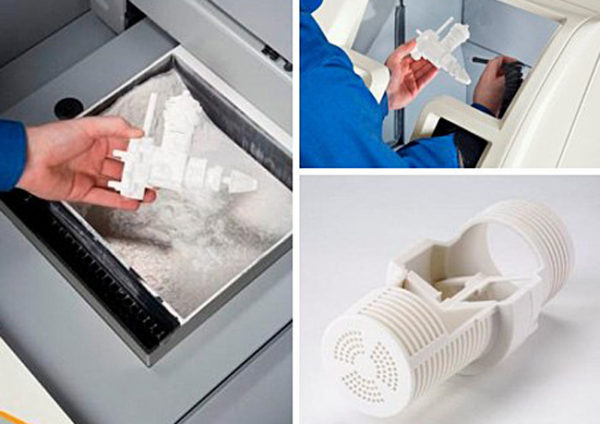
SLS
Selective laser sintering resembles the above described type of technology, but here laser powder is baked instead of photopolymer. You can not be afraid of breakage in the process of parts, and as a consumable it is likely to use steel, nylon, bronze, titanium, ceramics, glass, foundry wax and other materials.
Technology involves the creation of complex things. It is great, for example, to create any prototypes — for example, for jewelry. The unbaked powder will serve as a support for the overhanging elements - it means that it is not necessary to form any special supporting hulls.
3DP
The 3DP method consists of applying a glue to the material, followed by a layer of fresh powder and then everything is new. The result is a plaster-like material (sandstone). If you add paint to this glue, you get colored objects. The technology is safe for domestic and office use. For materials suitable glass, bone, rubber, and even consisting of sawdust powders. Can do and edible figures (using chocolate or sugar powders) - only in this case special food glue is taken.
Not without flaws - the end result may have a rough surface and low resolution.

Summarizing what was said
3D printing attracts a large number of people interested in it because of personal curiosity or for production purposes. For those who have no experience in this field, it will not be difficult to learn the art of bulk printing, both in virtual and real courses. It will be more important: for what specific purposes it is planned to buy such a device. The correct prioritization, combined with the knowledge of the technology used for a particular application, will make it possible to use the technology to the full.

/rating_off.png)











