What is a matrix of a digital camera
No camera can do without a matrix. Modern models are equipped with it almost all. This happened at the moment when digital analogs began to crowd out outdated film technologies. The camera matrix is one of the main components, without which the operation of the entire device as a whole is impossible, because its role, if not the key one, then at least can be considered one of the leading ones. It is the matrix that is responsible for the quality of the future image, color reproduction, clarity, fullness of the frame. Like other important elements of photographic equipment, the matrix has a number of basic parameters, which are usually taken as a guide when choosing a particular model.
Content
Matrix Types
The matrix of a digital camera is, first of all, chip. It converts light rays, which, having been refracted in the system of lenses and mirrors, fall on it. As a result of such a transformation, an electrical signal is obtained, which is displayed in digital form, forming a snapshot. For this entire process, special photo sensors located on the board itself are responsible. The greater the number of sensors that are sensitive to light, the greater the resolution, and, as a consequence, the quality of the final image.
There are matrices of the following types.
- CCD - type of camera matrixwhich literally stands for a charge-coupled device. In the English version - Charge-Coupled Device. Very well-known abbreviation, which, however, is not so common in our days. Many use devices based on LEDs with high sensitivity, based on the CCD system, but, despite the high prevalence, this type of chip is increasingly being replaced by more modern ones.
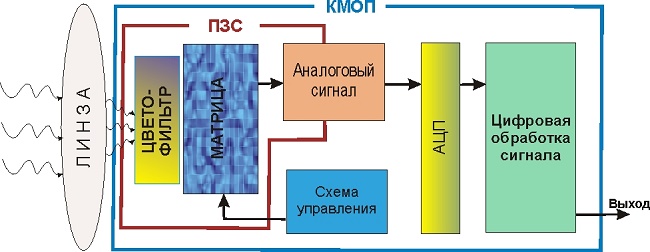
- CMOS matrix. Matrix format, commissioned in 2008. However, the history of the creation of this format goes back to the distant 93rd, when the APS technology was first tested. The CMOS matrix is a complementary metal oxide semiconductor.This technology allows sampling of an individual pixel in almost the same way as in a standard memory system; moreover, each pixel is equipped with an additional amplifier. Since this system is more modern, it is often equipped with an automatic adjustment of the exposure time of each pixel separately. This improvement allows you to get a full frame without losing the side borders, as well as without losing the top and bottom of the frame. The full-size matrix is most often made using CMOS technology.
- There is another type of matrix - Live MOS-matrix. It was released by the company "Panasonic". This chip operates with the help of technology, which are based on the MOS. MOS-matrix allows you to make high-quality professional images without a high noise level, and also eliminates overheating.
Physical matrix size
The size of the matrix camera - one of its most important characteristics. As a rule, it is indicated in inches as a fraction. Larger size means less noise in the final shot. In addition, the larger the physical size, the more light rays the matrix is able to register.The volume and number of rays directly affect the quality of the transmission of shades and tones.
Crop factor is a 35 mm film camera frame size ratio for a digital camera matrix.. The fact is that the process of creating a digital matrix is quite expensive, and therefore manufacturers have tried to minimize its size.
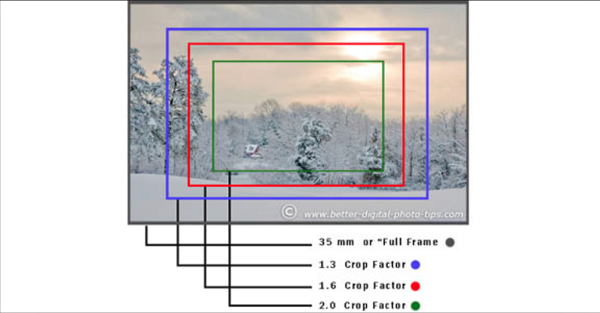
If you compare a photo taken with a single lens on a camera with a full-frame matrix and a camera with a “crooked” matrix, then in the first case the angle of coverage will be larger, and the image itself will be wider. It turns out that the cropped matrix cuts the finished picture, hence the name - cropped from English. crop (cut).
Most often, the cropping factor is used to measure the most accurate distance of the focus of the lens, installing it on various devices. This is where a concept such as equivalent focal length (EGF), which is calculated by multiplying the focal length (RF) by the crop factor. So, a lens with a full-frame matrix (crop = 1) and a lens with 50 mm DF will capture the same image size as the 1.6 cropped matrix with a 30 mm lens with DF.In this case, we can say that the EGF of these lenses is the same. Below is a table in which a comparison can be made of how EGF varies depending on the crop factor.
Number of megapixels and matrix resolution
The matrix itself is discrete. It consists of more than a million elements that transform the luminous flux coming from the lenses. In the characteristic of each model of the camera, you can find such a parameter of the matrix board as the number of photosensitive elements or matrix resolution, measured in megapixels.
One megapixel is equal to one million light-sensitive sensors that catch the rays refracted in the lenses. Of course, the more this parameter will be, the better the picture will be done.
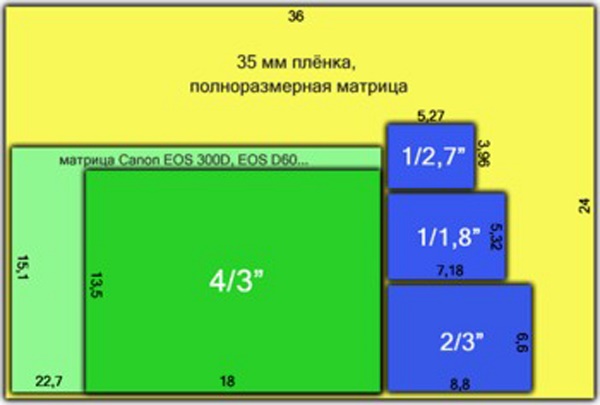
True, there is an inverse relationship. If the physical size of the matrix is smaller, then the number of megapixels should be proportionally smaller, otherwise the diffraction effect cannot be avoided: the photos will be blurred, without clarity.
The larger the pixel size, the more it is able to fix the rays falling on it. The size of the pixels is directly related to the size of the matrix, and affects mainly frame width. The greater the number of megapixels with the correct ratio of the dimensions of the matrix, the more rays of light I can catch the sensors. The number of fixed rays directly affects the original parameters of the material being converted: sharpness, color, volume, contrast, focus.
Thus, the resolution of the camera affects picture quality. The dependence of the resolution on the amount of pixels used is obvious. In the lens, with the help of a complex arrangement of optical elements, the necessary luminous flux is formed, which the matrix will then divide into pixels. Optical devices also have their own resolution. Moreover, if the resolution of the lens is sufficiently small, and the transmission of two luminous points, separated by one dark one, occurs as a whole, the resolution will not be so distinctly distinguished. This happens precisely because of the direct relationship and binding to the number of megapixels.
Important: a high-quality image is affected by both the matrix resolution parameter and the lens optics resolution. It is measured by the number of lines per 1 mm. The resolution reaches its maximum value when both indicators — the matrix and the lens — correspond to each other.
If we talk about the resolution of modern digital microcircuits, then it is made up of a pixel size (from 2 to 8 microns). To date, the market presents models with performance up to 30 mp.
Light sensitivity
In cameras with respect to the matrix, it is customary to use the term equivalent sensitivity. This is due to the fact that the true sensitivity can be measured in various ways, depending on the set of parameters of the matrix. But by applying signal amplification and digital processing, the user can detect high sensitivity limits.
The photosensitivity parameters demonstrate the ability of the source material to be converted from electromagnetic effects of the flow of light into an electrical binary signal. Simply put, show how much light is required to obtain an objective level of an electrical impulse at the output.
The sensitivity parameter (ISO) is most often used by photographers to demonstrate the possibility of shooting in low light conditions. Increasing the sensitivity in the instrument parameters allows to improve the quality of the final image at the required aperture value and shutter speed.ISO can reach values from a few tens to thousands and tens of thousands of units. The negative side of high sensitivity is the appearance of "noise" which appear as a frame grit effect.

How to clean the matrix at home
Dead pixels may not always be so. In fact, when a lens change occurs, debris particles can get onto the matrix, causing broken pixel effect". Cleaning the matrix of the camera is needed to prevent this effect, as well as for more comfortable working with the device.
Over time, especially if the device is operated for a long time in different weather conditions, the matrix can become covered with dust. If the tightness in the area of the lens mount is impaired, a small amount of moisture can get onto the surface, which can also negatively affect the quality of the frame. Cleaning can be entrusted to professionals from the service center, and you can do it yourself, at home.
It is important to remember that the room in which the procedure will take place should be as dusty as possible, without strong drafts.Before proceeding with the procedure itself, you must make sure that the battery is charged.
The first and easiest way to clean the glass surface of a silicon wafer chip is blowing dust. To do this, use the most common lens cleaner, it is sold in any major hardware store. Unfortunately, the use of a pear helps only when removing a light bloom of small dust grains of sand. For larger particles that could stick to the surface, something more solid may be needed.

If the pear did not help to cope with stains on the matrix, you can try to use special set for cleaning the glass surface. It costs a little more, but the cleaning efficiency is much higher.
- The first item in cleaning is the use of special vacuum cleaner. Its assembly does not take much time and is described in detail in the instructions for the kit. At the end of the device is a soft tip, so that damage to the device during operation is excluded. It is best to clean with a vacuum cleaner not only the glass surface, but also all the cavities that are accessible for cleaning.

- After cleaning with a vacuum cleaner, you can begin wet cleaning. It is carried out using special brushesone of which is wet, the other is dry. This type of cleaning is needed for dust particles, which, being wet, hit the glass surface, and having dried, attached to it, creating the effect of a “broken pixel”. Wet brush impregnated with a special solution that effectively removes dried grains of sand and dust, leaving no stains and stains. It is necessary to carry out on the glass with smooth gentle movements, only slightly pressing the brush itself. The remaining moisture will evaporate rather quickly itself. Even if a couple of drops remain on the glass after wet cleaning, they can be perfectly removed with a dry brush (brush).
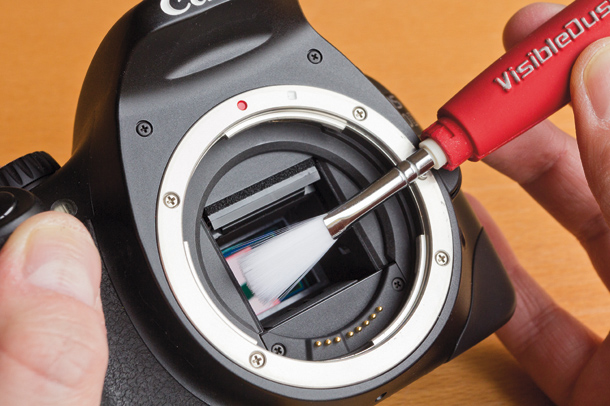

- The third stage is the final stage. dry brush on the matrix and make sure that it is clean.
After cleaning, you can try to take a test picture to make sure that the procedure was successful. To do this, close the aperture to the maximum value and take a snapshot of a blank white sheet, bringing the lens into a state of full defocusing. Then compare the quality of the pictures before and after.
It is quite simple to clean the mirror camera matrix; it does not require any deep knowledge or much experience, enough desire, some patience and knowledge of the basic principles of cleaning high-precision optical technology.
Conclusion
The matrix of the camera is the most important part of any modern DSLR. Without it, it is impossible to take a picture, and further use of the device depends on its parameters. If the matrix parameters are selected incorrectly, the camera will not optimally cope with its tasks. The matrix does not require any additional care, except for periodic cleaning of the glass surface.
It should be noted that photosensitive sensors are very fragile and do not survive the fall of the device even from a small height, therefore it is recommended to operate the camera with the utmost care and accuracy.

/rating_off.png)











