NFC technology: working principle and capabilities
NFC technology, which allows you to perform many daily routine operations using a smartphone, has become widespread in recent years. Shopping in stores, traveling by public transport, and identifying individuals when attending various events are just examples of the possibilities of NFC. In fact, the smartphone in our time has become a full-fledged document, combining identity cards, bank cards, email and many other attributes, without which you can now do in everyday life.
NFC is a wireless technology with a range of no more than 10 cm.

RFID allows you to transmit data from transponders for a fraction of a second (usually not more than 0.1 second). The obtained information is read and recorded. The data exchange rate in this case is no more than 400 kbps.
The principle of operation is as follows. Through a special antenna, the transmitter emits a constant signal.There is also an antenna in the sensor, and when both devices are within a radius sufficient to activate NFC, a magnetic field is generated in the reader coil. Its strength and current strength of the sensor is enough to establish the connection and perform the necessary operations. To ensure a stable signal in the smartphone, the antenna is attached to the back of the case under the cover.
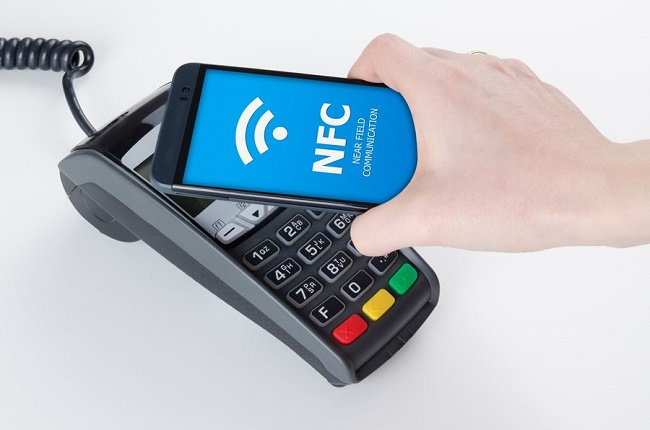

NFC technology is most often used for making payments, in which case the smartphone becomes an emulator of banking and other cards. The information about the calculations is stored on a special chip, through which the information is encrypted and the necessary transactions are started.
Another area in which NFC is used is the use of a gadget in reader mode. Through the smartphone, the user can receive additional information from special bar codes. For example, if the packaging with the goods is equipped with such a bar code, the customer can receive information on the composition or shelf life of the product.

/rating_off.png)