Inverter welding machines
One of the most durable and hermetic ways of joining metal parts is electric arc welding. This method has been actively used for over a hundred years. It consists in melting the edges of the elements being welded and filling the voids between them with the liquid metal of the welding electrode under the action of an electric current. Initially, bulky power transformers were used for this, reducing the mains voltage to the required 50-60 volts. Now commonly used inverter welding machine, which has a modern device and broad technical capabilities.
Content
The principle of operation of the welding inverter
The main difference of the inverter type welding machine is a more complex chain of transformations that a standard alternating electric current undergoes at a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 220 volts before it is applied to the electrode. First, it straightens and smoothes when passing a special filter. Then, quickly opening and closing transistors invert it into alternating current with an oscillation frequency reaching tens of kHz. Only after this stage, the current is transformed to the required 100-200A with a voltage of 50-60V for welding. Works at the exit high frequency rectifier, achieving passage of the direct current necessary for the most high-quality types of welding.
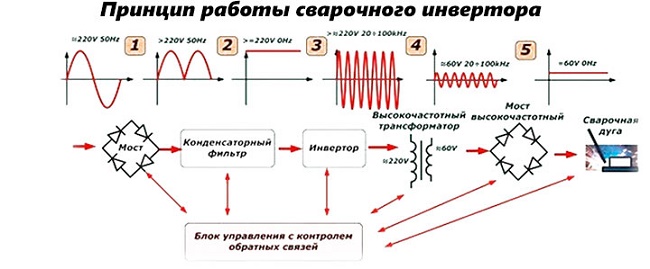
Control and adjustment of the outgoing values of welding inverter operation parameters is carried out by a transistor control unit. It forms the optimal characteristics of the current flowing to the electrode, which are necessary for all types and modes of welding.
The main difference between a welding transformer and an inverter is the conversion of low-frequency currents by a power transformer, which is realized only on large-sized devices,at the same time the high-frequency equipment of the inverter is characterized by compactness and low material consumption.

Benefits of Inverters
Comparison of welding inverters with devices of alternative designs demonstrates the compelling advantages of such equipment.
- Low weight not exceeding 10 kg, and the compact dimensions of most models facilitate their storage and transportation.
- No heat lossspent on heating the windings had a positive effect on the efficiency of the inverter, which, other things being equal, consumes about 1.5 times less energy than a typical welding transformer or rectifier ..
- Universal inverter has wide range of outgoing characteristicsthat allows you to select modes, including for welding stainless steel and non-ferrous metals.
- Even models for home and garden do not require long breaks in work on the cooling apparatus.
- Inverter for welding is equipped simple control system with a smooth setting of all the necessary parameters, which allows even a novice welder to achieve high quality welds.
There are inverters and disadvantages, which are relatively high price and strict requirements for storage and operation. They are sensitive to dust, excessive moisture and low temperatures.
Classification
AT production purposes Various types of inverters are used, differing in their functional features:
- for manual electric arc welding (MMA);
- for argon welding with tungsten electrode;
- for semi-automatic welding in an atmosphere of inert or active gases (MIG / MAG);
- semi-automatic devices for use in MMA and MIG / MAG modes;
- universal for work in different modes;
- air plasma cutting units.
In terms of performance and technical specifications, inverters for working with consumable electrodes are conventionally divided into three broad categories.
- Household mini-modelsdesigned for home and garden, which have the simplest equipment, are inexpensive and will serve well for occasional use.

Inverter welding WESTER MINI200
- Professionalable to cook for several hours a day, which is better to buy for production purposes, since they cost 300-400 dollars each and will not pay for themselves at home.

Welding inverter Wester Wz7 400 professional
- Semi-professional devices, occupying an intermediate position between the first two groups, which, if used reasonably, are suitable both for the house and for a small workshop.
What to look for when buying an inverter
The selection of a welding inverter is based on the welding conditions and the modes to which it should conform. First determined with input voltage. The overwhelming majority of devices are designed for 220 V power supply, but there are also models that are connected to the 380 V network. In the device passport it is designated as the allowable range: 220V + 15% - 30% or 160-240V. In rural areas with frequent voltage drops, this can be important.
The most important characteristic of the welding mode is the welding current: it directly depends on the thickness of the parts to be welded and the diameter of the electrodes used. In the domestic environment rarely have to cook products thicker than 10 mm. In this case, it is better to choose an inverter capable of delivering a current of 160-180 A. When welding sheets of carbon steel with a thickness of up to 20 mm, it is necessary to rely on 200 A. More powerful units should be purchased only for specialized workshops. The method of setting is also important.The possibility of smooth control in contrast to the discrete is always preferable to achieve high-quality seam.
The ease of ignition of the welding arc is associated with no-load voltage. For most models, it is in the range of 40 to 90 volts. The higher this figure, the easier it will be to cook.
With intensive use, a large impact on the performance of the unit has percentage of time at maximum currentdenoted by PV. A good device should have such an indicator at a level not lower than 70%. This means that during the production cycle of 10 minutes, 7 of them can be boiled under full load, and 3 minutes should be spent on replacing the electrode, cleaning the seam and cooling the device.
Additional functions implemented on welding inverters
The use of microprocessor control of inverter equipment with effective feedback allows you to implement additional options that facilitate the welding process. These should include:
- hot start, providing a short-term increase in voltage in the initial period of welding, which facilitates the burning of the arc;
- anti-sticking, dramatically reducing the load when the electrode is accidentally touched by the edges to be welded, thus avoiding the welding of the electrode, which is a common problem for beginners;
- arc boost, eliminating sticking of the electrode in the separation from it of a large drop of molten metal due to a short-term increase in current.
All of these properties of inverter welding machines have a positive effect on the convenience of working with them and the quality of the seams.

/rating_off.png)











