How does the SLR camera work?
The camera was invented in 1861 for receiving and storing still images. Initially in the device they were fixed on special plates, and later on the film. With the 70s of the 20th century begins the intensive development of digital technology. Classical (film) photographic devices gradually begin to fade into the background. To date, they have almost been supplanted by digital cameras. These modern devices allow you to take high-quality images. The most widely used are mirror, mirrorless and compact models. For those engaged in the creation of photographs, it is recommended to use the first two types of products. At the same time for this kind of activity requires knowledge of the camera device and the principle of its action.
Content
- 1 The principle of operation of cameras
- 2 Basic elements of a digital camera
- 3 Camera lens
- 4 Mount optics
- 5 Aperture and its functions
- 6 Mirrors work
- 7 Functions and types of valves
- 8 Pentaprism and viewfinder
- 9 Diffraction Digital Camera Matrix
- 10 Image stabilization systems
- 11 Brief description of the remaining parts of photographic equipment
- 12 Conclusion
The principle of operation of cameras
The principle of operation of digital and film photographic apparatus, in general, is identical. Strongly simplified his scheme can be represented as follows:
- after pressing the button, the shutter opens and the light reflected from the object enters through the lens inside the photographic device;
- as a result, a picture is formed on a photosensitive element (matrix or film) - photographing;
- the shutter closes, after which the device is ready to take further pictures.
The whole process of photographing takes place in a split second. Different models of photographic equipment due to their design features, its detailed flow differs.

Unlike film cameras in digital instead of photochemical preservation of images used photoelectric method. Its essence lies in the fact that the luminous flux is converted into an electrical signal, which is then recorded on the information carrier (digital storage device).
The captured image is immediately available for viewing on the liquid crystal display, which is very convenient for evaluating the result. It can be saved on a computer or laptop for later viewing, storing, editing, transferring (for example, via the Internet) or printing on photo paper using a printer.
Basic elements of a digital camera
A mirror digital camera is one of the most advanced in terms of construction and functionality of an extensive group of photographic equipment. On his example it is convenient to consider the device of photographic devices in general. This is due to the fact that you can get acquainted with the structural elements that are found in other types of this technology.
The main parts of the mirror digital photographic apparatus are:
- lens;
- matrix;
- diaphragm;
- gate;
- pentaprism;
- viewfinder;
- swivel and auxiliary mirrors;
- light-tight case.
Detailed the structure of the camera is presented below. It shows that the considered main parts are directly involved in the process of obtaining the image.
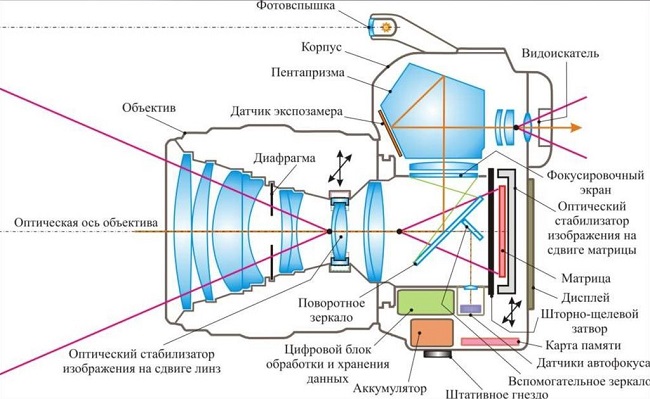
Without additional details, such as a photo flash, a memory card, batteries, a liquid crystal display, various sensors, it is also impossible for the camera to work and to get high-quality photos. But these structural elements are not directly related to the principle of the functioning of photographic equipment.
Camera lens
The lens is an optical system that consists of lenses located inside the rim. They are glass or plastic (in cheap models of technology). The luminous flux passing through the lens refracts and forms an image on the matrix. Good lenses allow you to get sharp, clear pictures without distortion.

New lens models can be equipped with electronic circuitscontrolling, for example, optical stabilizer, aperture. But on older cameras, electronics may not function.
The main characteristics of lenses are:
- Luminosity - parameter showing the relationship between the brightness of the object that is displayed, and the illumination of the image obtained in the focal plane (on the matrix) using the optical system.
- Focal length - is the distance in millimeters from the optical center of the lens to the mark of the focal plane (focus) in which the matrix is located. It depends on the viewing angle (field of view) of the optics and the size of the resulting image.
- Zoom - the ability of the optical system to approach distant objects (increase their image). It is determined by the ratio of focal lengths (maximum to minimum).
- Variety of bayonet.
On the marking of lenses, usually the first number (or a pair of numbers) indicates the focal length, and the second (or a pair) indicates the luminosity. Lens classification by focal length and viewing angle is shown in the following photo. A more universal type of optics is considered.
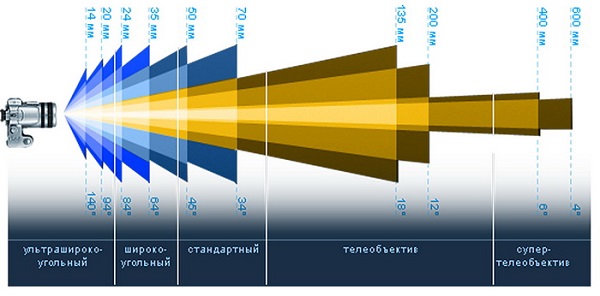
Important! Luminous efficiency of lenses depends on luminosity. The larger it is, the better the photo equipment and, accordingly, is more expensive. The optical system, which has a greater aperture, allows you to take pictures at shorter exposures than with a lower given figure.
Mount optics
The lenses are attached to the body of the camera with a bayonet. It is a special high-precision compound (often a standard type).Structurally, this mounting unit can be made in the form of a cap nut, equipped with cuts, or protrusions on the frame with the corresponding grooves on the housing. There are product models where the bayonet connection is represented by a large thread having a short stroke.
The main characteristics of the bayonet include:
- the diameter that affects the aperture ratio of the lens;
- working segment (shown schematically in the photo below), which determines the range of working focal lengths.
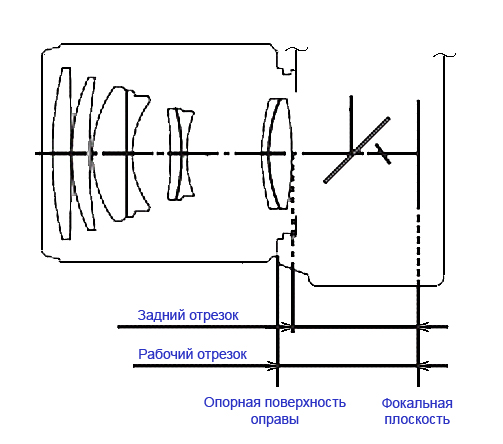
Aperture and its functions
Aperture is a mechanism designed to regulate the luminous flux falling on a matrix of a digital camera.. It is located between the lenses inside the lens.
Structurally, the part consists of a set of overlapping one petals (their usual number is from 2 to 20 pieces), which come in different shapes. The magnitude of their mutual shift relative to the base position determines the size of the resulting round (when fully opened) or polygonal (whenpartial) holes. Due to the fact that the mechanism opens and closes, the amount of incoming light changes. Expensive and high-quality optics equipped multilobe diaphragms.

The depth of field depends on the diameter of the aperture of the diaphragm (depth of field of the imaged space): the smaller the circle, the larger the depth of field. Such an interconnection allows photographers to create various effects when shooting, for example, to separate an object from the background.
In addition to the considered indicators, the aperture size of the diaphragm affects the parameters of the resulting image:
- aberration (error or error in the transfer of the image), the value of which is the smallest, when the diaphragm is closed as close as possible;
- diffraction (rounding by light waves of obstacles), expressed in reducing the ability of optics to reproduce images of objects that are located near (the indicator is called the lens resolution), while reducing the size of the light-transmitting hole;
- vignetting (decrease in illumination occurring from the center of the picture to its edges), most clearly manifested at the maximum open aperture.
The diaphragm is usually denoted by the letter “f”.The number next to it indicates the diameter of the hole. In this case, the smaller the number, the larger the size of the hole, denoted by it. The diameter of 2.8 at this time is the maximum on most lenses. Diffraction with aberration is balanced in apertures from f / 8 to f / 11. The lens has a maximum resolution.

Modern SLR cameras have lenses equipped with iris diaphragms of the jumping type. They are closed to the set value only at the immediate moment of shooting. To be able to estimate the depth of field of an image with a certain hole diameter, many SLRs equipped with a repeater. It is a mechanism for the forced closure of the diaphragm to the working value.
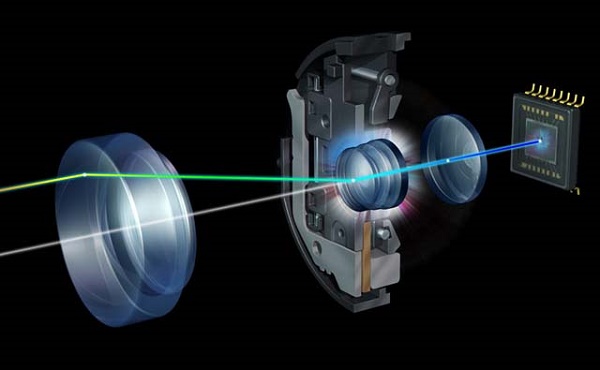
Mirrors work
The light that has passed through the opening of the diaphragm falls on the mirror. There the flow is divided into 2 parts. One of them enters the phase sensors (reflected from the auxiliary mirror), which are designed to determine whether or not the image is in focus. Then the focusing system issues a command to the lenses to move. In this case, they become so that the subject is in focus.Such self-tuning is called phase autofocus. It is one of the main advantages of DSLRs to mirrorless digital cameras. To see the mirror inside the case, you just need to remove the optics.
The second stream falls on the focusing screen (frosted glass). Thanks to this, the photographer can immediately assess the depth of field of the future picture and the accuracy of focusing. The convex lens located above the focusing screen increases the size of the resulting image. The mirror is removed after pressing the shutter, allowing light without obstacles to enter the matrix.
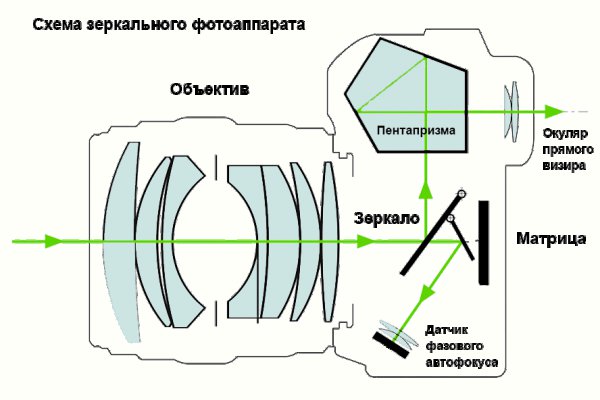
A whole category of photographic equipment is represented by models with a fixed translucent mirror. Its use allows you to use autofocus not only when taking pictures, but also during video recording in the “Live View” mode. Continuous sighting is also possible.
Functions and types of valves
After pressing the shutter, the shutter is also activated, which is installed between the mirror and the matrix. Its purpose is to regulate access to the matrix of light. The time during which the shutter is open is called shutter speed. During this time period, the exposure process takes place.
The shutters on the mirrors are of two types:
- mechanical (most common);
- electronic (digital).
Constructively mechanical shutters is a vertically or horizontally positioned 1 or 2 curtains opaque to the light flux. The main characteristics of such gates are speed and lag. Under the latter understand the speed of opening the curtains after pressing the trigger.
Opening and closing of the curtains occurs very quickly (in a split second) at the expense of electromagnets or springs. The shutter speed is the amount of time it takes to get a snapshot after pressing the shutter. Mechanical shutters have a limit of operation. Extracts from about 1/8000 second are obtained using digital shutters.
Electronic shutter - this is not a separate device, but the principle of controlling the exposure (amount of incoming light) by the matrix. Exposure in this case is the time interval between its zeroing and the moment of reading information from it. The use of electronic shutters is characterized by the possibility of achieving shorter exposures without the use of expensive mechanical analogs.
Models of photographic devices with a combination of electronic and mechanical types of valves are considered more perfect. In this case, the first is used for short exposures, and the second - for long. Also, the mechanical shutter protects the matrix from dust.
The amount of light coming inside the camera, controlled by the aperture, and the shutter speed shutter are the basis of the photographing process. Due to the combination of these indicators in various versions, photographers achieve different effects.
Pentaprism and viewfinder
The light flux, passing through the focusing screen, enters the pentaprism. It consists from two mirrors. Initially, the image from the swivel mirror comes upside down. Pentaprism mirrors turn it over, giving the final image to the viewfinder in the normal way.
The viewfinder is a device that allows the photographer to pre-evaluate frames. Its main characteristics are:
- lightness (depends on the quality and light transmission properties of the glass from which it is made);
- size (area);
- coverage (in modern models reaches 96-100%).

The pattern of movement of the light flux in the viewfinder of the camera
SLR cameras can be equipped with the following types of viewfinders:
- optical;
- electronic;
- mirror.
Optical viewfinders most common. Such devices are located near the lens lens system. Their advantage is the lack of energy consumption, and the disadvantage is some distortion of the image falling into the frame.
Electronic devices - This is a miniature liquid crystal (LCD) screen. The image is transmitted to it from the camera matrix. The electronic viewfinder can be used even in strong sunlight, because it is located inside the case. But while working, he consumes electricity.
Mirror Viewfinders are considered the best, because they are able to provide the highest contrast, the quality of the contours of objects. Such devices are transferred to digital photographic devices from film analogues. The image seen by the photographer is formed by a turning mirror.
There are models without viewfinders. In them, the photographer sights the images using an LCD monitor. The disadvantage of such screens is that it is almost impossible to look at them in bright sunlight. Also, monitors may have a small resolution.
Diffraction Digital Camera Matrix
The DSLR matrix is an analog or digital-analog chip with photosensors. The latter are photosensitive elementsthat convert light energy into electrical charge (proportional to the brightness of the light). In this way, matrices translate an optical image into an analog signal or into digital data. Which then go through the chain converter-processor-memory card.
Important! For receiving pictures in color corresponds to the light filter. It is installed in front of the microcircuit.
The main characteristics of the matrices are:
- resolution;
- the size;
- photosensitivity (ISO);
- the relationship between signal and noise (a cluster of randomly located points of different colors, the appearance of which is associated with a lack of illumination of objects).
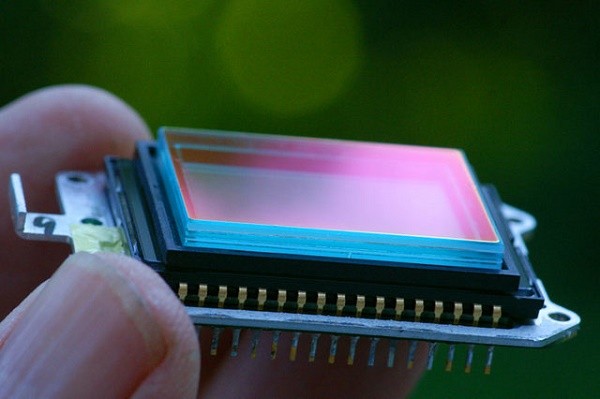
Under by permission they understand the number of photosensitive elements in the part, measured in modern devices with megapixels (corresponding to a million photosensors). The greater their number, the better small details will be transferred to the photo.
From matrix sizemeasured diagonally, depends on the number of photons that it can catch, as well as the presence of noise in the resulting image. The larger this parameter is, the better (less noise). The diagonal details in the sought-after models of photographic equipment is 1 / 1.8 -1 / 3.2 inches.
Light sensitivity of matrices is in the range of 50-3200. Large values of sensitivity allow shooting in low light conditions, for example, at dusk or at night. But this increases the noise level. The optimal ISO level is considered to be from 50 to 400. An increase in sensitivity is accompanied by an increase in noise.

In the mirror photographic technique, two types of matrices became popular:
- full frame (same size as 35 mm film frame);
- truncated (with a reduced diagonal).
Matrices differ from each other in formats that are as follows:
- Full Frame - full frame (35 × 24 mm);
- APS-H - matrix of professional cameras (29 × 19-24 × 16 mm);
- APS-C - used in models of consumer-grade products (23 × 15-18 × 12 mm).
Full-frame matrices are larger than truncated. They are equipped with professional camera models.
Image stabilization systems
Due to camera movement when taking a picture or due to hand shake, blurry frames are obtained. The image stabilizer is struggling with this phenomenon (not available in all models). It is of three types:
- optical;
- with a movable matrix;
- electronic (digital).
The first is a lens unit mounted in the lens that is controlled by special sensors. Systems with moving matrix (for example, "Anti-shake") suggest its fixation on a moving platform. They are considered less effective than optical stabilization.
Electronic vr (vibration suppressor) involves the transformation of only pictures by the processor. The digital stabilizer functions with any lenses.
Brief description of the remaining parts of photographic equipment
The presence of a flash allows you to highlight objects located in the foreground close to the photographer.Usually, such devices built initially are of small capacity. For this reason, semi-professional and professional photographic devices are equipped with a connector that allows you to connect additional flash units.

The functions of the camera expands the use of flashes capable of suppressing red eye. Also convenient is the presence of several of their main operating modes:
- automatic;
- forced;
- slow sync;
- without flash.
To make self-portraits or eliminate camera vibrations, use self-timer. This device creates a time delay between pressing the shutter release and its actual triggering.
On a note! During long-term photography, it is recommended to replace a number of models of DSLRs instead of rechargeable batteries using an adapter connected via the dc in connector. This is only possible if you have access to a 220 V network.
Camera processor performs the following functions:
- controls flash, camera interface, autofocus;
- calculates the exposure;
- processes data from the matrix;
- adjusts the sharpness, sensitivity, contrast, white balance, noise and several other parameters of the picture;
- saves an image on a memory card, compressing files;
- provides communication with external devices (for example, a computer).
When processing digital data by the processor, they are stored in RAM. Removable media in the form of memory cards of various formats (for example, SecureDigital - SD) are used to permanently store information.

Due to the presence control buttons You can manually control different settings, for example: adjust the shutter speed with aperture, set the sensitivity of the matrix, white balance. This allows you to control the entire process of photography, to create the desired effects.
Conclusion
SLR cameras allow you to take high-quality images due to the presence of large matrices. Therefore, they are used in their activities by professional photographers and amateurs who are seriously engaged in photography. The most important factor in the popularity of mirror photographic equipment is also interchangeable optics, which makes it possible to carry out photographing through a telescope, endoscope or microscope.

/rating_off.png)











