How to choose a good radiation background dosimeter
A household dosimeter can be very useful if you know how to choose and use it correctly. The term "dosimeter" means a rich variety of techniques for measuring the level of radiation. Different models and their modifications may differ according to the principle of operation, design, functionality and design. Most often, when choosing the best of any devices, the first thing to consider is the user's needs. Dosimeters, radiometers or dosimeters-radiometers are not an exception here, the purpose of use radically decides which model is best suited.

Content
Professional or household
Any dosimeter is designed to ensure the safety of human health, so you need to decide on the class of equipment.First of all, it is worth understanding the difference between household and professional models.
Dosimeters or radiometers professional level Specialists working in potentially dangerous conditions: at nuclear power plants, factories for the production of weapons or medical equipment, in banks. Many organizations buy background radiation meters for employees of other specialties in order to protect their health. Devices are subject to strict control of production, and their minimum requirements are regulated by law.

Each specific model is entered in the register of Rosstandart. If the device is not entered in the register, it is not professional, despite the parameters, the assurances of the seller or manufacturer.
The capabilities of professional radiometers or dosimeters are in most cases superior to household-level devices. They are able to register even a small excess of the rate of radioactive radiation, and large doses are determined at a distance. In addition, they are an order of magnitude more accurate, the error of the average model will not exceed 15%, and the stated parameters can be trusted.
The principle of operation of the dosimeter or radiometer domestic class most often similar to professional versions. Devices differ in relatively affordable cost, they are smaller and easier to use. Not every model is capable of separating beta and gamma radiation, and there are practically no alpha particle meters, but there is rarely a real need for this. The error and accuracy of data recording is naturally lower, but this is quite enough for determining and measuring radioactive studies.

Types of counters
A radioactive background detector or counter is the basis of a dosimeter or radiometer. There are different types of counters designed to register alpha, beta or gamma radiation, and in most cases - their combinations, such as beta and gamma.
What detectors are used in various dosimeters?
- Mica Geiger counters (end) register alpha and beta radiation.
- Popular gas discharge SBM-20 and their modifications. Their miniature versions of the SBM-10 are used for small devices, but it should be noted that the dosimeter will only show critical exceeding of the norm. Sensors register beta and gamma radiation.
- Thermoluminescent lamps or TLD they are small in size and are most often used in individual dosimeters. An effective area of application is measurement of the cumulative dose from X-rays.
- Scintillation crystals, according to the manufacturers, it is more sensitive than all the rest (about a Geiger counter about 20 times), in addition, they are smaller and can be installed even in pocket models. If we take into account that the crystals themselves inside the device are wrapped in foil, then they are useless for recording alpha radiation. Most often they are used in radiometers to search for a source of radiation.
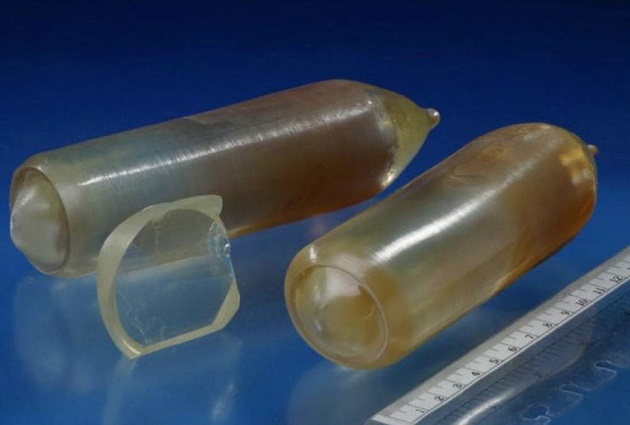

CdWO4 Crystal Scintillation Elements
- Pin diodesinstalled in small plugs to the telephone or small “dosimeters-toys”. Such meters are hardly suitable for at least some adequate measurement, they are sensitive only to very critical radiation.
The device of the dosimeter can contain any of the listed detectors, the type of counter always affects the cost and the area of use of the device.
Overview and Classification
Simply, all household dosimeters, radiometers or dosimeters-radiometers are called “dosimeters”, but this is not entirely correct.If the term is appropriate for the combined models, then radiometers are instruments of a different purpose.
The key difference between the two meters is that the dosimeter records the radiation dose and its power over a set period of time, for example, per minute or per day. Radiometers measure the current radiation power (density of a stream of radioactive particles) of a source or various samples. In other words, a radiometer is a device for searching a source of radiation or determining the level of contamination “here and now”, and a dosimeter is a meter of the received (accumulated) dose. Types of dosimeters have a large number of different models; choosing a good one should pay attention to those devices that combine both the first and second in themselves.
Individual dosimeters
Under the name "personal dosimeter" or "alarm device" it is customary to understand a small compact device, no larger than an ordinary key fob. Threshold ion radiation detection informs the user with a sound or vibration signal. Models with thermoluminescent counters have a light signal, which is quite convenient.
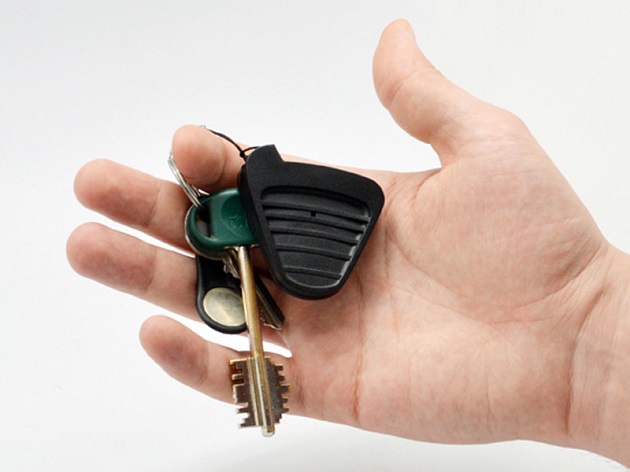

Dosimeter Geiger Keychain MT2033
Structurally, individual models are very simple, they do not have a display or a wide option. They are worn on a belt or in a pocket, when they hit the danger zone, the dosimeter sends a signal, and all data is stored in memory. The technical parameters of the alarms are low, and full change information can be obtained only by connecting the device to a PC or smartphone.
Depending on the modification, individual dosimeters measure neutron, photon, beta or gamma radiation.
Individual dosimeters used for securitywhen the user is near a potentially dangerous area, but does not set a research goal. On the other hand, some modern models are capable of this. A keychain-dosimeter, fixed on clothes, will quickly inform about the threat and increase of the rate of ion radiation, will measure the accumulated dose on the skin.
Pocket versions
The classic household dosimeter should be convenient and compact, because pocket models are widespread among the population. There are many modifications of such devices, but all of them are united by several main characteristics:
- small size - the device should fit in a regular pocket;
- powered by battery or conventional batteries;
- registration of beta / gamma radiation;
- the presence of the display;
- simple interface.

Pocket dosimeter of the new generation Atom Fast
The range of use of such devices is small: measurement of the natural background radiation with a dosimeter in order to identify the dose excess, record the indicators. Diagnostics of various building materials or products is acceptable, but the device can only detect high activity.
There are also more technologically advanced models, for example pocket scintillation dosimeter Atom Fast. This is a compact pocket dosimeter with no display, but with wide functionality. Synchronization with the gadget allows you to set thresholds, make graphs, put data on the map.
Portable dosimeters
Portable devices are in many ways similar to pocket versions, outwardly they differ mainly in slightly larger sizes. The rest is the same radiometers or dosimeters-radiometers with a small display and an acceptable set of options:
- registration of gamma radiation;
- in rare cases - measuring the flux density of beta particles;
- data archiving;
- synchronization with computers or various devices for output and analysis of the collected information;
- various types of signal: light, sound, vibro or display on the display.
A portable radiation dosimeter most often combines a dosimeter and a radiometer. Most often, such devices are a compact version of the device to search for a source of radiation.
Large sizes allow you to install up to four detectors in one housing, which increases the accuracy and area of scanning, reduces the time of measurement of radioactive background. To remove data from a portable device does not require specialized equipment, with the exception of a PC, tablet or smartphone.
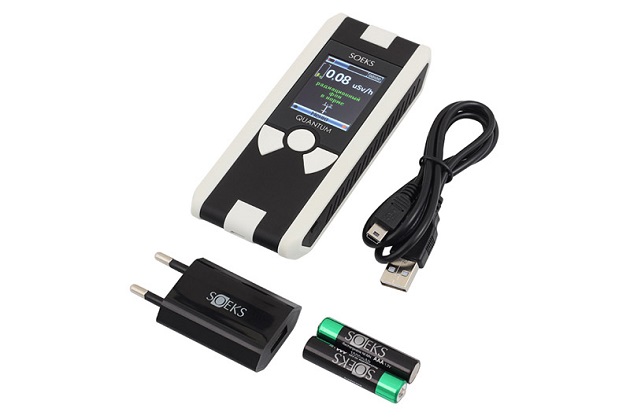

Among the wide range you can find both household and professional dosimeters-radiometers. Latest news such as SOEKS Quantum can be attributed to the golden mean; it is a functional and compact dosimeter with two SBM-20-1 counters and a color display, made in the Rosstandard registry. Despite the assurances of manufacturers, the device can hardly be called professional, it is not capable of separating beta and gamma radiation, but captures the high activity of products, building materials or other objects.
Tips for choosing
Before choosing a dosimeter, you should decide for what purpose it will be used. To determine the increased background radiation can any of the above models. If this is the only task, the choice of the dosimeter can be based solely on cost.
There is another classification of devices, according to the type of their work. Before buying it is useful to know which dosimeter will correspond to the tasks.
- Low threshold low sensitivity indicators - such a dosimeter can determine the presence of a radioactive background from any object, but no more.
- Signaling devices - these are the same indicators, but with threshold values, about which the dosimeter informs with a sound or vibro-signal (for example, Neiva-ИР-001).
- Gauges equip more sensitive and accurate radiation sensors. They provide users with detailed information on registered radiation changes. This is the optimal dosimeter for measuring the radioactivity of objects, for example, MKS-03SA can be used to study building materials or jewelry.
- Search devices used to detect sources of radiation.They are not as accurate as gauges, but very sensitive to any changes in the background. As a detector, as a rule, they use scintillation crystals. In simple terms, they pick up radiation at a distance, and vibrations will determine the direction to the source. Scintillation dosimeters respond to gamma radiation, in rare cases - to “high beta”.
- Spectrometers - This is a more complex technique. In addition to the radiation source, they are able to determine the type of isotope that caused the increase in radiation Devices of this level are more expensive than household ones in 10, take, for example, laser dosimeter LD-07.
It is good if two or more meters are installed in the dosimeter, such wide-range instruments work faster. The SBM-20, SBT-11, SBT-9 and Beta have recommended themselves as highly sensitive sensors.
Pay attention to the upper threshold of measurements - its recommended value is from 10,000 μR / h. Devices with a small upper value may simply not determine a high level of radiation, while the indicator either does not register it at all, or underscores the real indicators several times, which is extremely dangerous for a person.
If the choice is between the GMS-20 and face mica sensor - choose the second, firstly, they are more sensitive, and secondly, they are able to register “soft beta radiation”. Their only drawback is brittleness; they should be handled with care, except for sudden pressure drops, shocks, vibrations, vapors from liquids or contact with mica.
Scintillator "search engines" in the domestic environment is extremely rarely required. If there is such a need, you need to pay attention to the size of the scintillation crystal: the larger it is, the more sensitive the device.
Refuse to purchase retired military dosimeters, you need to choose among modern models. At best, the device will not work, at worst it can be dangerous. Different variations with pin diodes or applications for smartphones have some real basis on the title of “dosimeter”, but in practice they are useless.
Meter Operation
It is quite simple to make sure that it is working or to check how the dosimeter works, just look at what the instrument shows.
The natural radiation background varies from 5 to 15 μR / hour, granite emits about 35 - 90 μR / hour, and potassium fertilizer will show from 20 to 40 μR / hour.
Information on how to use the dosimeter or radiometer is indicated in the user manual. In most cases, home appliances are easy to use and have an intuitive interface.

/rating_on.png)