How to repair welding inverter do it yourself
Inverter welding machines are gaining more and more popularity among welders due to their compact size, low weight and reasonable prices. Like any other equipment, these devices can fail due to improper operation or due to design flaws. In some cases, repair of inverter welding machines can be carried out independently, having studied the device of the inverter, but there are breakdowns that are fixed only in the service center.
Content
Welding inverter device
Depending on the models, welding inverters work both from a household electrical network (220 V) and from a three-phase (380 V). The only thing that needs to be considered when connecting the device to a household network is its power consumption. If it exceeds the capacity of the wiring, then the unit will not work when the network is flat.
So, the following main modules are included in the device of the inverter welding machine.
- Primary rectifier unit. This unit, consisting of a diode bridge, is placed at the input of the entire electrical circuit of the device. It is the alternating voltage supplied from the mains. To reduce the heating of the rectifier, a radiator is attached to it. The latter is cooled by a fan (intake) installed inside the housing of the unit. Also, the diode bridge has protection against overheating. It is implemented with the help of a thermal sensor, which, when the diodes reach a temperature of 90 °, breaks the circuit.

- Condenser filter. It is connected in parallel to a diode bridge to smooth out AC ripple and contains 2 capacitors. Each electrolyte has a voltage margin of at least 400 V, and a capacitance of 470 μF for each capacitor.
- Interference suppression filter. During the processes of current conversion in the inverter, electromagnetic interference occurs that can disrupt the operation of other devices connected to this electrical network. To remove interference, a filter is installed in front of the rectifier.
- Inverter. Responsible for converting AC voltage to DC. Converters operating in inverters can be of two types: two-stroke half-bridge and full bridge. Below is a diagram of a half-bridge converter having 2 transistor switches based on devices of the MOSFET or IGBT series, which can most often be seen on inverter devices in the middle price category.
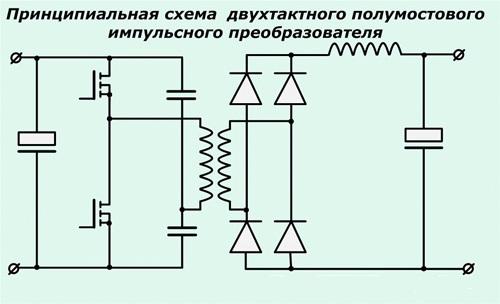 The circuit of the full bridge converter is more complex and already includes 4 transistors. These types of converters are installed on the most powerful devices for welding and, accordingly, on the most expensive ones.
The circuit of the full bridge converter is more complex and already includes 4 transistors. These types of converters are installed on the most powerful devices for welding and, accordingly, on the most expensive ones.
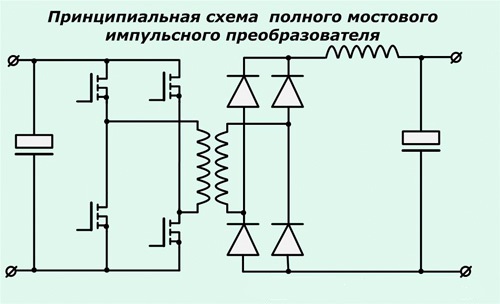
Just like diodes, transistors are mounted on radiators for better heat removal from them. To protect the transistor unit from voltage spikes, an RC filter is installed in front of it.
- High frequency transformer. It is installed after the inverter and lowers the high-frequency voltage to 60-70 V.Due to the inclusion of a ferrite magnetic circuit in the design of this module, it became possible to reduce the weight and reduce the size of the transformer, as well as reduce power loss and increase the efficiency of the equipment as a whole. For example, the weight of a transformer having an iron magnetic circuit and capable of providing a current of 160 A will be about 18 kg. But a transformer with a ferrite magnetic core with the same current characteristics will have a mass of about 0.3 kg.
- Secondary output rectifier. It consists of a bridge, which consists of special diodes, reacting at high speed to high-frequency current (opening, closing and restoring takes about 50 nanoseconds), which ordinary diodes are not capable of. The bridge is equipped with radiators to prevent its overheating. Also, the rectifier has protection against power surges, implemented as an RC filter. At the output of the module are placed two copper terminals, providing a reliable connection to them of the power cable and the ground cable.
- Control board. All operations of the inverter are controlled by a microprocessor, which receives information and controls the operation of the device with the help of various sensors located in almost all nodes of the unit.Thanks to microprocessor control, ideal current parameters are selected for welding various kinds of metals. Also, electronic control saves energy by supplying accurately calculated and metered loads.
- Soft start relay. To prevent the rectifier diodes from high current of charged capacitors from burning during the inverter start-up, a soft start relay is used.
How the inverter works
Below is a diagram that clearly shows the principle of operation of the welding inverter.
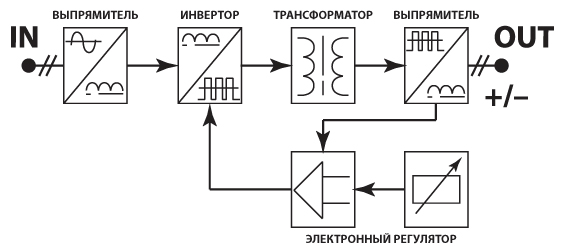
So, the principle of operation of this module of the welding machine is as follows. The primary rectifier of the inverter receives voltage from a household electrical network or from generators, gasoline or diesel. The input current is variable, but passing through the diode unit, becomes permanent. The rectified current goes to the inverter, where it is converted back to AC, but already with changed characteristics in frequency, that is, it becomes high-frequency. Further, the high-frequency voltage is reduced by the transformer to 60-70 V with a simultaneous increase in current.In the next stage, the current enters the rectifier again, where it is converted into a constant one, and then it is applied to the output terminals of the unit. All current conversions controlled by a microprocessor control unit.
Causes of inverter breakdowns
Modern inverters, especially those made on the basis of the IGBT module, are quite demanding of the rules of operation. This is explained by the fact that when the unit operates, its internal modules generate a lot of heat. Although both radiators and a fan are used to remove heat from power units and electronic boards, sometimes these measures are not enough, especially in low-cost units. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly follow the rules that are specified in the instructions for the device, implying a periodic shutdown of the unit for cooling.
This rule is usually called “On Time” (PV), which is measured in percent. Not observing the PV, overheating of the main components of the apparatus and their failure occurs. If this happens with the new unit, then this failure is not subject to warranty repair.
Also, if the inverter welding machine is working in dusty rooms, dust accumulates on its radiators and interferes with normal heat transfer, which inevitably leads to overheating and breakage of electrical components. If it is impossible to get rid of the presence of dust in the air, it is often necessary to open the inverter case and clean all the components of the apparatus from accumulated dirt.
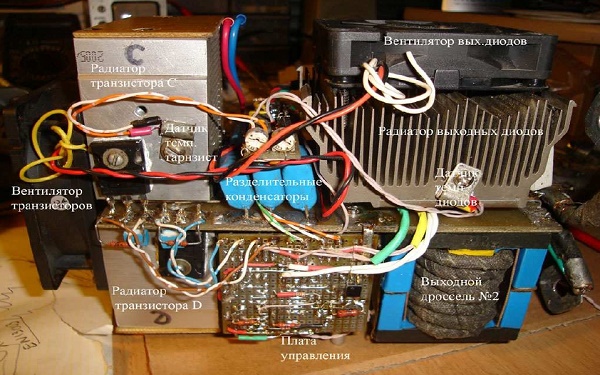
But most often the inverters fail when they work at low temperatures. Failures occur due to condensation on the heated control board, as a result of which a short circuit occurs between the details of the electronic module.
Features of repair
A distinctive feature of the inverters is the presence of an electronic control board, therefore, only a qualified specialist can diagnose and eliminate a fault in this unit.. In addition, diode bridges, transistor blocks, transformers and other parts of the electrical circuit of the device may break down. To do the diagnostics with your own hands, you need to have certain knowledge and skills to work with measuring instruments such as an oscilloscope and a multimeter.
From the above it becomes clear that, without having the necessary skills and knowledge, it is not recommended to start repairing the device, especially electronics.Otherwise, it can be completely incapacitated, and repair of the welding inverter will cost half the cost of the new unit.

Main unit malfunctions and their diagnostics
As already mentioned, the inverters fail due to the impact on the “vital” blocks of the device external factors. Also malfunctions of the welding inverter may occur due to improper operation of the equipment or errors in its settings. The following faults or interruptions in the operation of inverters are most common.
The device does not turn on
Very often this breakdown is caused network cable malfunction apparatus. Therefore, you must first remove the cover from the unit and ring each wire of the cable with a tester. But if the cable is OK, then a more serious diagnosis of the inverter will be required. Perhaps the problem lies in the standby power source of the device. The technique of repairing the “duty” by the example of the Resant brand inverter is shown in this video.
The instability of the welding arc or spatter
This fault may be caused by improperly setting the current for a particular electrode diameter.
You should also consider welding speed. The smaller it is, the smaller current value must be set on the unit's control panel. In addition to the current strength that corresponds to the diameter of the additive, you can use the table below.
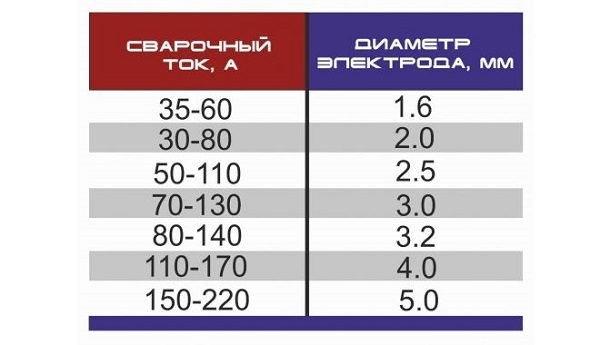
Welding current is not regulated
If the welding current is not regulated, the cause may be regulator failure or a breakdown of the wires connected to it. It is necessary to remove the housing of the unit and check the reliability of the connection of the conductors, as well as, if necessary, ring the regulator with a multimeter. If everything is all right with it, then this breakage can be caused by a short circuit in the choke or a failure of the secondary transformer, which will need to be checked with a multimeter. If a fault is detected in these modules, they must be replaced or rewound to a specialist.
Large power consumption
Excessive power consumption, even if the device is unloaded, causes, most often, interturn closure in one of the transformers. In this case, repair them yourself will not work. It is necessary to refer the transformer to the master for rewinding.
Electrode sticks to metal.
This happens if mains voltage drops. To get rid of the sticking of the electrode to the parts being welded, it will be necessary to select and adjust the welding mode (according to the instructions for the device). Also, the mains voltage may subside if the device is connected to an extension cord with a small wire cross-section (less than 2.5 mm2).
Often, the voltage drop causing the electrode sticking occurs when using an oversized network extension. In this case, the problem is solved by connecting the inverter to the generator.
Overheating is burning
If the indicator is on, it indicates that the main modules of the unit are overheating. Also, the device can spontaneously turn off, which indicates thermal protection triggered. So that these interruptions in the operation of the unit do not happen in the future, again it is required to adhere to the correct mode of the duration of switching on (PV). For example, if PV = 70%, then the device should work in the following mode: after 7 minutes of operation, the unit will be allocated 3 minutes to cool down.
In fact, various breakdowns and the reasons causing them may be quite a lot, and it is difficult to list them all. Therefore, it is better to immediately understand what algorithm is used to diagnose the welding inverter in search of faults. How the device is diagnosed, you can find out by looking at the following training video.

/rating_off.png)











