How to work automatic welding machine
The demand for welding semiautomatic devices in the welding equipment market continues to grow every year. This is due to their obvious advantages: affordable cost, a wide range of operating modes, ease of setup and operation. However, a beginner master is not always able to figure out how to properly use a semi-automatic. The first thing you need to know is the device and the principle of operation of the unit, as well as the basic recommendations for choosing a wire for welding.
Content
Device and principle of operation of the semiautomatic device
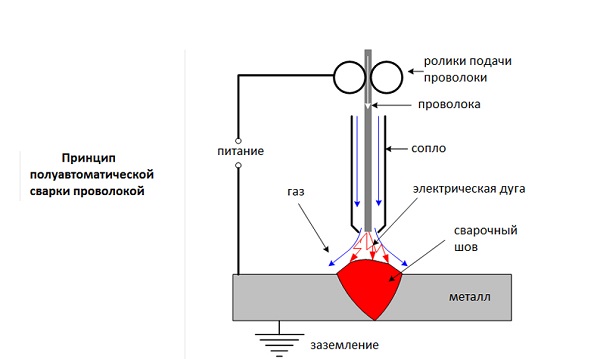
The main purpose of a semi-automatic welding machine is arc welding with the use of a melting electrode, which is blown with protective gas. The device is used to join low-alloyed and low-carbon steels, both long and intermittent seams.
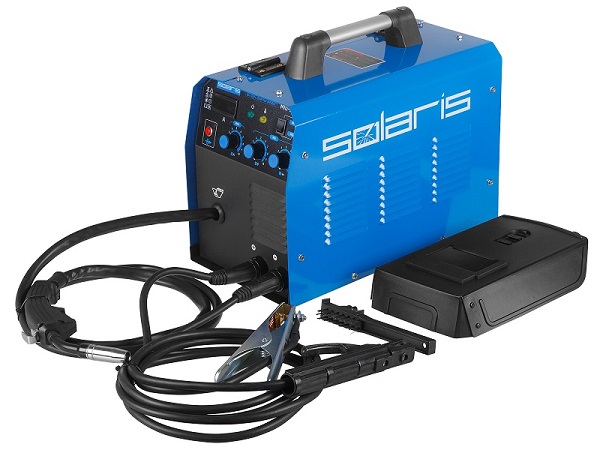

This equipment is designed to work in closed, well-ventilated areas at air temperatures from -10 ° C to + 40 ° C.
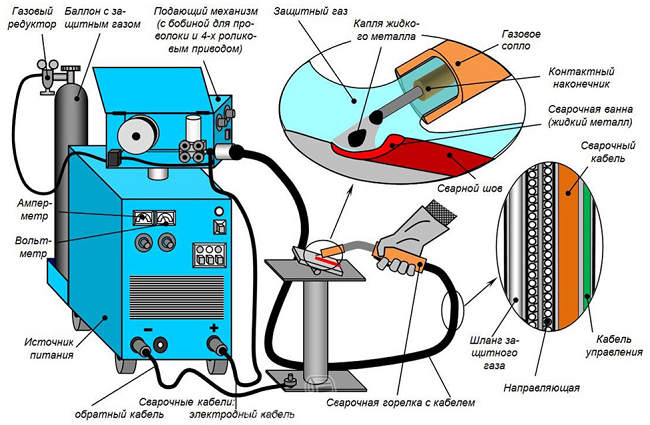
The semiautomatic device consists of following items:
- main unit producing welding current of the required size;
- wire feed unit;
- a welding torch with a connected cable through which the power wire passes, a gas hose, a control wire and a guide for the wire electrode.
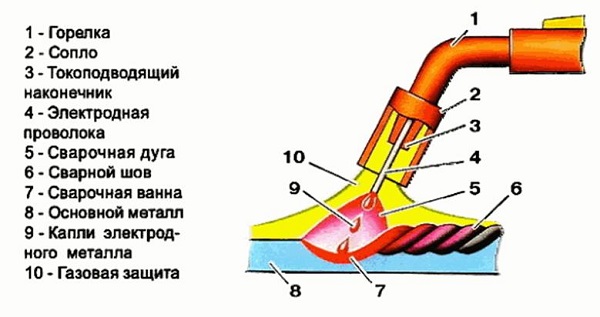
The principle of operation of the unit is as follows. By pressing the start button located on the torch handle, the supply of electrode wire (4), current and protective gas through the nozzle (2) begins. The current to the wire flows through the conductive tip (4). When it comes into contact with the base metal, an electric arc arises, which begins to melt the electrode. Drops of the electrode metal, falling on the base metal (8), form a seam (6). At the same time, the welding bath (7) is under blown with protective gas (10), which prevents oxygen and nitrogen from entering it from atmospheric air.Thanks to the gas protection, the weld is durable and of high quality.
The operation of the semiautomatic device is possible without protective gas. In this case, an electrode wire having a special powder coating is used. At high temperatures, this coating evaporates, and the resulting gases perform a protective function for the weld pool.
Electrode wire selection
Electrode wire is a snap, without which the welding machine will not be able to work. It is served using a special mechanism and performs the function of an electrode.
For semi-automatic there are two groups of materials for welding:
- solid wire;
- cored electrode wire.
There are more than 76 types of the first variant. But more often, only a small part of them is used. Other types of equipment are highly specialized and are used in production. The main thing to consider when choosing a wire is the type of metal from which the structure will be welded. Most often, it is necessary to boil low-carbon and low-alloy steels using non-copper-coated and copper-coated wire.
Copperplated wire is the most popular among welders due to anti-corrosion coating. But not everyone knows that during the smelting of copper in the air get harmful evaporation. Non Copper Wire is more harmless and has anti-corrosion coating.
Also used on semi-automatic cored wirethat does not require the presence of protective gas during cooking. Electrode wire has a special marking, for example, such: SV-08G2S. It is deciphered as follows:
- SV - welded wire;
- 08 – means that the mass fraction of carbon in the composition of the tooling is 0.08%;
- G - this letter denotes manganese, which is in the composition of the wire;
- 2 - the figure indicates that the manganese content is 2%;
- WITH - this letter indicates the presence of silicon in the equipment, if after the letter there is no number, then it contains no more than 1%.
The following is a table in which the letter designations of all the additives that make up the welding wire are decoded.

For example, using the table, one can decipher the marking CB-06Х21Н7БТ, which means: the welding wire has 0.06% carbon, 21% chromium, and nickel - 7%; The wire is alloyed with two metals, niobium and titanium.
For welding low alloy steels (this is 90% of the total metal) wire 08G2S with a diameter of 0.6 mm is used. It can be used both in everyday life and for body repair. In addition, it can be used on units with a current up to 500A. For welding stainless steels use wire brand Sv01H19N9. Aluminum and copper are boiled in argon medium, corresponding in composition to the wire. Aluminum is boiled with grades SV-97, CB-A85 and CB-AMts. For welding of copper used equipment brands SV-97, CB-A85 and CB-AMts.
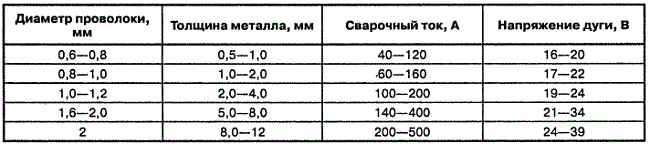
The diameter of the electrode wire is selected in accordance with the thickness of the metal being welded.
Semiautomatic welding rules
First of all, when starting to work with a semiautomatic device, the parts intended for connection must be well cleaned of paint and rust. Also clean the place to which the clip for the mass will be attached.
How to hold a burner
You can hold the burner with one hand, but the quality of the seam will be better if you use both. One hand serves as a support, while the other holds the burner.
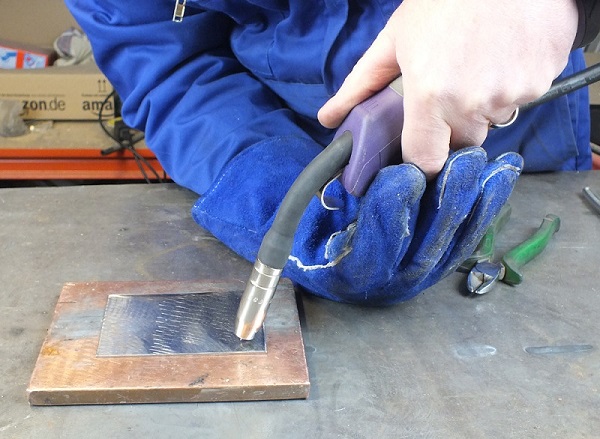

With this method it is easier to control the angle and distance of the burner from the workpiece, as well as to carry out the necessary movements to form a high-quality weld. To keep your hands free, you need use welding maskwhich is fixed on the head.
The ideal angle when operating as a semi-automatic does not exist. Usually, to connect the blanks lying in the same plane, the inclination of the burner (from the vertical position) at 15-20 degrees is used. Connecting parts that are at an angle to each other, the torch tilt of 45 ° is used. With the acquisition of experience, each welder selects for himself the most convenient angle of inclination of the tool, taking into account various situations.
Motion Burner
For the formation of high-quality seam there are many ways of movement of the torch.
- For metals 1-2 mm thick applied wavy-zigzag movement. Thus, the arc captures both sheets of metal and does not have time to burn it. As a result, the seam is sealed and durable.

- For welding metals of any thickness apply a straight seam, excluding any movement to the side. But in this case, the operator is required to have a certain experience so that when the torch moves, the arc evenly acts on both the mating parts.
- If work is coming metal less than 1 mm thick, it is necessary to reduce the current strength and wire feed speed, as well as to use a wire of smaller diameter. Welding should occur in short pulses, with a pause between them of about 1 second. A pause is needed to cool the metal and drain the next segments into a monolithic seam.
- If mating long, thin details, then welding is carried out with short segments or points located at a certain distance. Also, to avoid deformation of parts, you can cook alternately, short segments, with different ends of the mating segment.
Welding speed
This is the speed of movement of the electric arc along the interface of parts, and is controlled by the operator of the semiautomatic device. The speed of movement of the tool should correspond to the arc voltage, wire feed speed, metal thickness and the required seam shape. At high speeds of movement of the burner, a lot of sprays are formed, the protective gas remains in the rapidly hardening seam and causes the formation of pores in it.With a slow speed of movement of the burner, an excessive electric arc is formed into the material, which can burn it through. In addition, when connecting massive parts formed thick seam. The following figure shows what the seams look like at different torch speeds.

Gas flow rate
The gas supply should be sufficient to provide blowing wire. With a weak gas flow, the seam will not be protected from oxidation. But even at high flow rates, protection will be insufficient due to turbulence. All these deviations from the norm make the seam porous and fragile. Therefore, it is very important to achieve a smooth gas supply, so that the flow does not cause turbulence and fully protects the welding site.
Wire length
The wire, before it touches the metal, must come out of the tip by 6-13 mm. From this value depends resistance and temperature of this piece of electrode. The stronger the reach of the wire from the tip, the smaller will be the size of the arc. As a result, the seam is thick and narrow, with low penetration into the metal.If the length of the tooling is reduced, the arc penetration into the metal will increase, and the seam will become thinner and wider.
Polarity
By polarity in welding equipment is meant the direction of the current in its circuit. With direct polarity, a negative charge is supplied to the wire, and a positive charge is applied to the welded part. With reverse polarity, the opposite is true: the wire is a plus, and the workpiece is a minus.
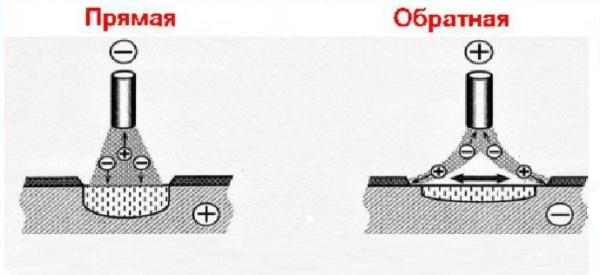
Important! When working without protective gas, flux-cored wire uses the method of direct polarity, and with gas - reverse polarity.
Sound when welding
Listening to the sounds of welding is important, especially for beginners when learning. The correct sound when welding with a semiautomatic device resembles the sound of meat roasting in a pan. When a “hissing-buzzing” sound is heard, it means that there is a balance between the current settings and the wire and gas feed rates. The sound change when the device is operating can be affected by:
- poor contact between the weight clamp and the part;
- the presence of frozen spray on the tip of the burner, preventing the normal flow of gas;
- poorly cleaned from rust or paint area of welding.
Safety measures at work
During the work with the welding equipment it is necessary to observe the following security measures.
- The welder must protect all parts of the body from splashes of hot metal on them. For this used work clothestightly covering exposed areas of the body, as well as protective gloves. Clothing should be made of dense material that can withstand the ingress of hot splashes. In no case should clothes be made of synthetic fibers, which, when exposed to high temperatures, begin to melt. Such material instantly burns through, which can cause burns to the welder.
- Since hard ultraviolet radiation is produced during welding, it is necessary to protect the eyes from it using mask with tinted glass. Not so long ago, masks with “chameleon” glass appeared on the market, which darkened when bright light appeared. Also, other parts of the body must be protected from UV light.
- Shoes should be closed to prevent hot splashes from falling into it.
- The room where the welding work is carried out must have forced or natural ventilation (the presence of windows that can be opened). Inhalation of fumes and smoke generated during the welding process has a detrimental effect on human health.

/rating_off.png)











