Power and energy of the electric kettle
The modern world can provide a huge variety of manufactured technical products, differing both in size and in their power. Electric kettles are no exception. Many people are interested in the question, what is the power consumption of the kettle and, as a result, the power consumption of this type of equipment.
Content
What determines the power of the electric kettle
Power of the modern electric kettle can vary from 700 to 3000 watts. Although power is a fundamental characteristic, it is necessary to understand that the amount of energy consumed per month depends on many factors:
- flask volume;
- type of heating element;
- water quality, etc.
Power consumption depends on the installed heating element.In total there are 2 types of heaters used in the production of this kind of technology.
- TEN open type. Such a heating element is a coil mounted in the housing of the device and having direct contact with a liquid. A device with this type of water heating will emit much less noise and perform its task much faster than the “closed” analogue.
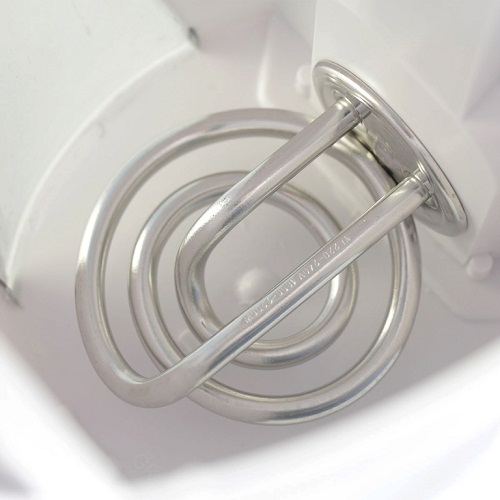

- TEN of the closed type. Usually this type of heaters is a special heating plate, which is mounted on the bottom of the case. Although the indicators of water heating time and noise level exceed analogs of "open", devices with such an element form much less scale.
The average heating time in a kettle with a closed heating element is about 3 minutes. Despite the lower heating rate, modern models are represented by this very design. Devices with open heating elements heat up the liquid a little faster - in 2-2.5 minutes.
The rate of heating is also influenced by the materials used in the manufacture of the device. Kettles from metal do their job the fastest. But their body warms up strongly during operation, which requires additional power consumption (for heating the metal). Glass The teapots also heat up quickly, but the glass itself does not heat up as much as metal. Ceramics Lose a little in the matter of heating rate, but it retains heat much better. The water inside the ceramic kettle will still be hot for a long time.
The amount of energy consumed
How much energy does the kettle consume? At first glance, it is hard to believe that an iron and a kettle in a house can take up the lion's share of the money spent on electricity. The average power of an electric kettle is 1.5-3 kW / h. Assuming that the average heating time is 3 minutes, and you use it 4 times a day, we will calculate how much such a device consumes:
kW / month = 3 * 0.2 * 30 = 18 kW / month.
For comparison, an example is given of the average energy consumption of basic household appliances:
- washing machine - 20-25kw / month;
- computer - 30 kW / month;
- refrigerator - 30 kW / month;
- TV - 35 kW / hour.
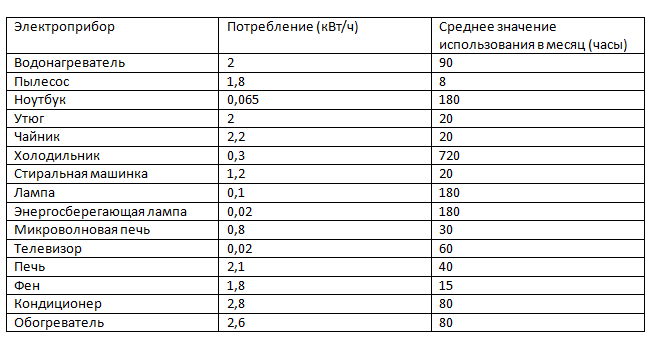
As you can see, the kettle is not such a big power consumption. But if to be a little more attentive and count the amount of time that all devices work, it becomes clear that the kettle and the iron consume the maximum amount of energy for the minimum amount of time!
How to save power consumption
So, the kettle can be attributed to quite economical devices in terms of energy savings. However, following some recommendations, you can slightly reduce consumption.
- If you do not use a kettle - unplug it. Even in standby mode, the technician consumes a certain amount of electricity.
- Boil only the amount of water that you now need for tea or other purposes. After all, in order to heat 2 liters of water, the energy will take 2 times more than heating 1 liter. It makes no sense to pour water to the maximum mark to drink one cup of tea.
- Regularly clean the device heater (and indeed the entire inner surface) from scale. The presence of deposits makes the process of boiling water longer and, therefore, more energy-intensive. In addition, the heating element can fail at all if there is a large layer of scale on it.
- If you think that boiling water on an electric stove is more economical - you are mistaken. In this regard, the kettle wins significantly - it will heat the water faster and with less energy.

/rating_on.png)











