Everything you need to know about the plotter
Today, almost every home and office desktop computer is equipped with a printer: the need to print documents literally on the fly occurs quite often. But the capabilities of a conventional printer or multifunction device (MFP) is not always enough. If a simple printer is quite suitable for outputting regular A4, this will not be enough for large format printing. Then the plotter comes to our rescue. Translated from the Greek language, it is a device for constructing an exact graphic pattern on a wide format (up to A0). Differently, such devices are also called plotters.
Content
General information about plotters
The fundamental difference between a plotter and a conventional printer (or MFP) is that in addition to printing on regular paper, the plotter is able to work with various types of consumables, as well as cut printed products. Custom printer models cannot work with large paper sizes (A1, A0), but the plotter can. In addition, in plotters, specialized paper is most often used, impregnated with dyes and reagents, which are manifested during a chemical reaction. Conventional MFP implies the use of classic consumables.

What is a plotter in a broader sense? As has already become clear, this type of device is used when the need arises to print products on large sheets of paper. A good example is ads, advertising posters and billboards, printing drawings.
However, the plotter can be used not only for printing paper, their area of application is much wider. The wave is real, for example, woodwork or vinyl, you can find a textile plotter and even a food 3d machine. But the cost of such models is very high, so they are not widely spread.

Textile plotter Mimaki Tx300P-1800
The most popular models of plotters work with paper, film, vinyl, plastic, performing layouts for various purposes.
For cutting printed products there are special devices - cutters, and they are also referred to as plotters. Less commonly, there are 2 in 1 devices that combine both possibilities in themselves - printing and cutting. Let's try to figure out how these devices are classified.

Solvent plotter cutter VersaCAMM VS-300i
Basic classification
At the moment there is no generally accepted classification of plotters, which is widely used everywhere. Despite this omission, there are several principles for distinguishing plotters. One of them - by appointment. The separation will be small, only two versions:
- cutting;
- typing.

Plotter Epson SureColor SC-T7200 with PZK and ink
Printing apparatus not able to cut printed products on their own. As a rule, for this you have to buy a second device, or initially consider a device that combines these functions (if necessary). For cutting already printed promotional products is intended cutting plotter - cutter, it is suitable for stickers, films, and in rare cases even for vinyl products.
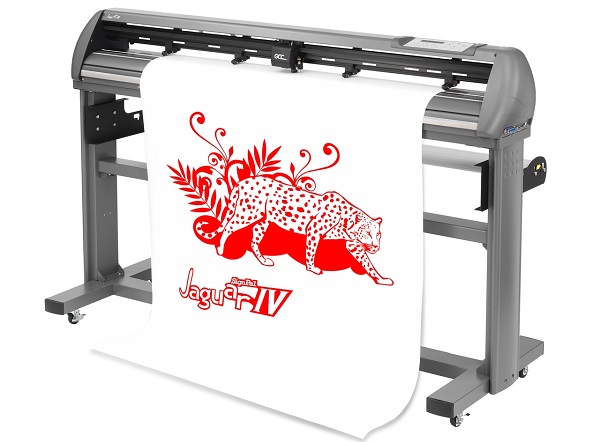
Cutting plotter Vektor HC-1290
By type of construction plotters are:
- flat (tablet);
- roll;
- laser.

Tablet Plotter
Flat fixes the sheet, and the cutting of the film is performed by a moving carriage with a knife, moving according to a given pattern. In case of rolled the device, the carriage moves in different directions, thereby cutting out the necessary pattern during the material feed. Laser The cutter has a flat design, but, unlike the first option, instead of a carriage with a knife, a high-precision laser is responsible for cutting. Of course, the quality of such products will be much higher: it is possible to work out smaller and more precise details.
The printing plotter is the most affordable unit for creating small quantities of advertising or holiday products in an office environment. For storage and maintenance of such a device does not require a storage room or any special conditions, which can not be said about consumables.
Most often, paper or vinyl, on which prints occur according to a given layout, is a material impregnated with chemical solutions that do not tolerate sudden changes in temperature.
Therefore, when storing consumables for a printing plotter, it is strongly recommended to observe the temperature conditions.

Color vinyl rolls
The difference in plotters in the form of the drawing block
In the case of a drawing block, classification is easier. The following varieties exist:
- feather;
- jet type;
- laser type;
- electrostatic type;
- direct output;
- thermal transfer of information.
Let us consider in more detail each of the above types of technology.
Feather
The principle of operation of the pen plotter is simple: the image is applied to the base with a pen, which can move only in two directions. As a dye can be used a special pencil or liquid paint. The latter happens solvent and ecosolvent. What does it mean? Solvent inks are composed of solvents, which allows you to create drawings on PVC surfaces for which they were created. Ecosolvent paints also contain solvents, but less aggressive and toxic. They do not emit a pungent smell when working and are spent more economically.

For the movement of the pen in these plotters is responsible electric motortherefore, when creating drawings and drawings, they make a lot of noise. Another impressive minus pen plotters - low print speed. However, there are pluses:
- high quality of the received images;
- Saturated color and good contrast (with color printing).
Jet
In the jet plotter, the same technology is used as in the printer: printing is carried out by applying a set of small colored dots of 4 primary colors (CMYK). Inkjet plotters are popular because provide many benefits:
- high speed;
- good resolution;
- affordable service and consumables;
- optimal cost.

Inkjet models can be with ciss (system of uninterrupted ink supply). This quality is very important in the conditions of continuous or extreme fast typographical printing, when there is no time to refill a suddenly ended cartridge.
Laser
The laser plotter functions exactly the same way as the printer. We can say that this is a widescreen laser MFP. The basis lies electrographic technologybased on the photoelectric effect of photosensitive semiconductor layers of materials containing selenium, as well as on the effects of electrostatic fields. The image has a so-called.intermediate carrier (spinning drum with selenium deposited on it), which can be charged to an extremely high potential - hundreds of volts. With the help of a light beam, this charge is removed, forming an undeveloped electrostatic image attracted by magnetized fine toner. In the future, everything is mechanically transferred to the prepared paper.
Laser plotters are able to print an image in minutes, thanks to which they have gained massive popularity in both the advertising and printing business.. However, their cost is quite high compared with the first two types.
Electrostatic
An electrostatic plotter is somewhat similar to a laser. Its principle of operation is also based on the formation of latent images (electrical), the so-called. "Potential relief". Unfortunately, the disadvantage of this technology is that special printing is required for printing. electrostatic paper, thoroughly coated with dielectric and impregnated with hydrophilic salt. Such paper requires constant storage conditions, such as moisture, to maintain electrification. The slightest violation can lead to its damage.
Another disadvantage of electrostatic printed plotters is the very high cost of service devices themselves, the acquisition of consumables. The advantages include the stability of the finished product. The image obtained with the help of an electrostatic plotter is resistant to UV rays, is stored for a long time without losing brightness, and also has a high degree of protection against other external climatic conditions.

Direct output
Direct output plotter is also needed. specialized paper, without which their operation becomes impossible. Such paper is specially impregnated, and along the edges a narrow line is left of the “comb” of mini heaters. Heating is carried out while the paper is being fed from the roll. The color change occurs at the places of heating and depends on temperature.
Unfortunately, this printing technology is black and white. Direct output is not capable of providing colors, only a few shades of gray.
At the moment, consumables for direct output plotters have become available and are widely used in printing. Many archival vaults order the printing using direct output. This is due to the fact that the finished product has long shelf life and minimal sensitivity to external influences. Printing is carried out on paper, tracing paper and film.

With thermal transfer
Devices operating on the principle of thermal transfer are distinguished by the fact that between the heating element and special paper (including a film of different levels of transparency) is placed color matrix. Its thickness usually does not exceed 4-10 microns. The color matrix is placed close to the paper, to which part of the ink passes when heated. The coloring layer is made of wax and is not fusible.
In one pass one color is applied. Color correction is achieved in four full passes. Unfortunately, in connection with this we have to recall expensive consumables and the need for their frequent replacement. So, to create a color image it takes four times more ink than to draw a black and white image. It is because of this factor that this printing technology has not gained mass popularity. Most often, thermoplotters are used where it is necessary to create a three-dimensional image (for example, cartography) with high quality color rendering. In addition, this technology is used to create high-quality presentations.

Plotters "two in one"
A printing plotter with a cutting function is often called a hybrid or cutter. Despite some confusion in terminology, with the device data devices everything looks quite simple. Most often we are talking about a roll-type printed plotter with the possibility of cutting products. Such a combination of functions under one body is very convenient, especially when it comes to cutting film or paper immediately after printing products. In this case, it turns out to use one device instead of two, which greatly simplifies the process.
The release of such devices is engaged, in particular, the company Cricut. Although among their products there are ordinary plotters.
Specifications plotter cutter may vary depending on the requests. Basically when choosing such devices are guided by the following indicators.
- The degree of cutting widthAs a rule, it reaches 1000 mm. This is enough for the manufacture of most types of promotional products. For the manufacture of more specialized orders using large-format plotters, but most everyday needs can cover devices with a width of 500 to 720 mm.

Plotter cutter Roland TrueVis VG-540/640
- Cutting accuracy no less important. The thinner the material needed to be cut, the greater the precision of the blades will be required. Dependence in this case is direct. Of course, the greater the accuracy, the higher the price of such a cutter.
- Optical characteristics also important for this type of device. The most common positioning of optics is the presence of a specialized sensor capable of making marks on an already printed layout. Using the indicated contours, you can cut the material of any complexity. Such an optical sensor works by tying to the dimensions (coordination grid) of the source material. Having become attached by the size, the blade will be able to cut paper or a film precisely by the size and a bend, repeating the smallest nuances of drawing.

- Blade pressure. Everything is simple here: the stronger the pressure of the blade on the material, the thicker the paper or film the blade can cut. For handling ordinary paper, a pressure of 350 g will suffice. If it is meant to work with a harder material, such as vinyl, then such pressure will not be enough. For vinyl, the degree of pressure on the knife should not be less than 400-500g.
- Cutting speed. If everyday tasks do not include urgent cutting of printed products, then you should not consider a model with high speed. Overpayment for this option will be very substantial.
In addition to the characteristics discussed above, plotter cutters are distinguished by the presence of a display, a network pointer, a transverse knife, a basket for materials and a holder for rolls.

How to use different types of plotters
That's where there really is no limit to the imagination, so it is in the application of modern plotters. Of course, the main request comes from meeting the needs promotional products and typographic materials. Slightly smaller percentage is occupied by all kinds of archival and cartographic documents, where the consumer is more interested in the high quality of the printed product than in its quantity.
Today, the industry of commercial use of plotters is developing very actively and successfully. in the field of individual entrepreneurship: small photo salons, private studios, working on individual orders. Such workshops take orders for work on felt, fabrics, for scrapbooking - all this is made using a plotter.

For specific tasks that require a special approach, you can even use latex cutting material, but it should be noted that not all models can work with it.
The material for printing may have special properties, the limiter in this case is only the client's imagination. Almost anything can be printed on the surface of the material. In some cases, the application of paint is already on volume parts (for example, mapping using colored feathers). Examples of various uses are mass, ranging from posters printed on vinyl material, to individual "stretching" wallpapers made of innovative materials, which are painted with the help of a modern cutter-cutter, and later also are cut.
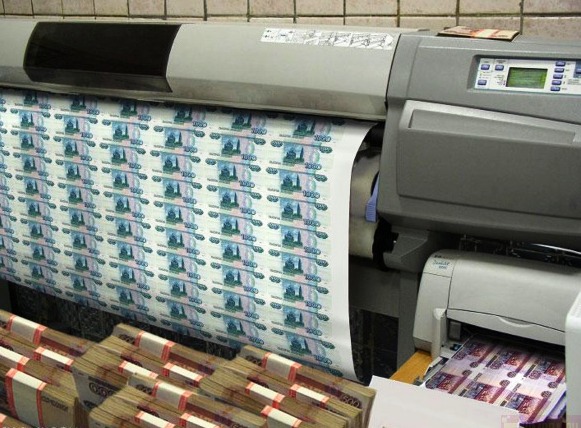
Another area of application plotters - printing of bank notes. They are made on cutting plotters, which initially mark and cut bills. The same applies to the printing of any government documents with the brand "state sign". Large volumes of printing are always carried out on a large-format technique, after which they are cut and delivered as they are ready to their destination.Even the paper on which the passport data is then printed, prints and cuts the plotter, the data are entered later, at the local passport office.

Documents, clothing, advertising signs, posters and banners are all hard to imagine without a device for printing and cutting. It can be said without exaggeration that this type of equipment moves entire industries and social organizations forward, ensuring their interaction.
Conclusion
Despite the fact that there are many types of plotters, one thing remains unchanged - their mass demand. Every day, this type of equipment covers the needs of a variety of promotions, ads and projects. That plotter allows a person to express their emotions more vividly and efficiently, as they deserve. Despite the high cost of consumables, the use of plotter cutters remains relevant. Rarely, when an industrial machine is idle idle for more than one day, most often the device is maximally loaded at weekends, during the day, and at night. And this is easy to explain - only the plotter is able to work with large formats, printing all the necessary information on them.

/rating_off.png)











