The real power consumption of air conditioning
Climate technology brings home the desired atmosphere. However, this will occur only with the constant inclusion of the device. That is why the very first question that interests potential users will be: how much electricity does a constantly-running air conditioner consume?
Content
What should be considered to determine the indicator
A bit of theory: in any air conditioner there is Heat pump, which pumps heat from one room to another, in particular, from an apartment to the street. It needs a certain amount of electricity to function. To know this figure, you need to understand: each conditioner has two characteristics: consumption and cooling / heating power (cold and heat output).These values are usually indicated in the passport of the device.
For information: the power consumption of the split-system shows how much energy the air conditioner consumes from the network, and the cooling / heating power - how much the system does useful work.

The measurement of both of these quantities is calculated in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). Again, these data are individually indicated in the document of each device: they are indicated in the figures “before” and “after” (in the second case we are talking about heat and cold). On any unit and in the manual, this information is presented to it, but recorded in the form indicators of heat (COP) or cold (EER). And the higher this final figure, the lower will be the power consumption.
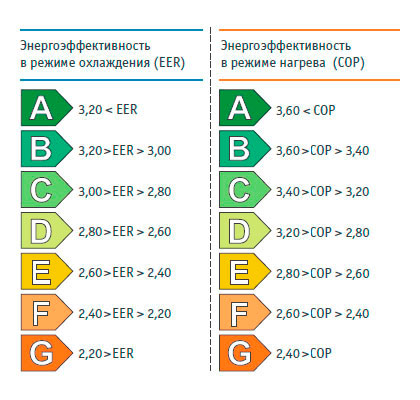
It should be aware that the indicators specified by the manufacturer may differ from the real ones. The fact is that at the enterprise all calculations for the split-system were carried out with the doors and windows closed. In practice, conditions are usually far from ideal. Another good news: any such device will consume three times less energy than it does. The fact is that the consumption of electricity will go only to the freon circulation and its transformation.
Knowledge of indicators for EER and COP helps determine energy efficiency classes. The most economical consuming device will belong to class A. In total there are seven such gradations, and they end with the marking G.
Other important factors
There are other parameters that affect the waste of electricity when operating a split system.
- Compressor potential (at lower speeds, less energy is consumed). The most profitable are inverter models.
- Real air conditioning consumption will show temperature difference (street with room). The costs for heating a room in forty-degree frost will be much higher than for cooling a room in the unbearable summer heat.
- Cooling loads in split system.
- Various additional functions device.
Consumption calculations
Many people mistakenly believe that air conditioning consumes a lot of energy, but in comparison with other devices that have been connected to the network for months, the amount of electricity consumed by the climate equipment turns out to be less. For example, the energy consumption of an air conditioner of a household class for a standard room with an area of 15-20 m2 is from 0.3 to 1 kW (minimum and maximum).It should be noted that the climatic equipment does not work all the time, but is turned on only to maintain the temperature in the apartment within certain limits, and if you add up the energy consumption per month, the amount is not too large.
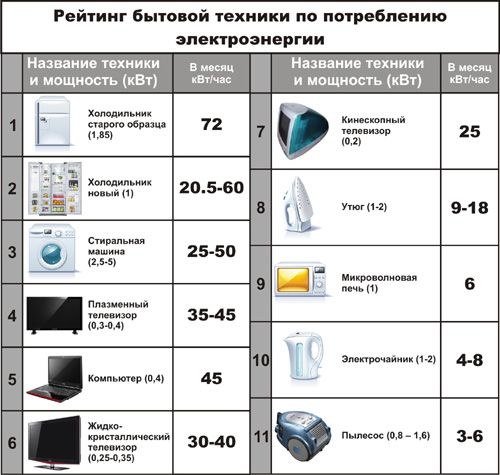
There is no universal formula, with one hundred percent accuracy answering such a question, how many kilowatts the equipment will spend. And, first of all, because, again, it is impossible to predict any temperature in the room (at the same time as the one outside). Also, we do not know with what frequency it is planned to turn on the device. However, approximate calculations of how much energy will be spent can be done - for this we need to take a sample. daily rate of expenditure.
The estimated work of a conventional split-system operating on the start-stop principle can be 6 hours. If the indicated demand is 800 W per hour, then 4.8 kW will be spent per day. It means that a day of cooling will cost 21 rubles (at a price of 4.32 rubles per kWh). This speaks of 630 rubles per month, which will have to be added to the cost of electricity.
These data may increase by several times if the device operation takes 24 hours a day (for example, if the apartment is located on the sunny side).
How to reduce the cost of air conditioning
Experts offer consumers the following figures: air conditioners with a capacity in the range of 2 to 3.5 kW will consume from 0.5 to 1.5 kW / h. But before switching on it is important to know some values:
- the power consumption of the air conditioner for which the socket is designed (the Russian one is suitable for current at 6.3 A / 10A, and the foreign one 10A / 16A);
- power that electrical wiring can withstand;
- parameters of protection plugs that protect the network from overloads.
There is a difference between household or industrial appliance planned to deliver. Air conditioning in the apartment power will not exceed 2400 W (and will also have a single-phase connection). In contrast, semi-industrial and industrial units can consume electricity up to several hundred kW (the connection must be three-phase).
There is one piece of advice that can help reduce power consumption at the buying stage. It's about acquiring inverter model. If you use such a system, the waste will be reduced by as much as 40% without losing the power of the device. The daily consumption of such an air conditioner will not exceed 0.5 kW, and the monthly fee will be about 390 rubles (six-hour work schedule).If you turn on around the clock, it will, of course, increase by 4 times, but again it will be much lower than that of the usual stop-start of climate technology.
Most popular air conditioners in 2018
Split system Electrolux EACS-07HAT / N3
Split system Haier AS12NS4ERA / 1U12BS3ERA
Split system Haier AS09NS4ERA / 1U09BS3ERA
Split system Mitsubishi Electric MSZ-DM25VA / MUZ-DM25VA
Monoblock Electrolux EACM-09CG / N3

/rating_off.png)











